Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus KLDS 1.0207 Exerts Antimicrobial and Cytotoxic Effects in vitro and Improves Blood Biochemical Parameters in vivo Against Notable Foodborne Pathogens
- PMID: 33072056
- PMCID: PMC7541842
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.583070
Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus KLDS 1.0207 Exerts Antimicrobial and Cytotoxic Effects in vitro and Improves Blood Biochemical Parameters in vivo Against Notable Foodborne Pathogens
Abstract
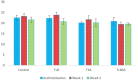
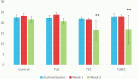
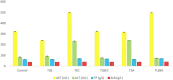
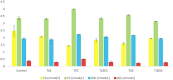
Globally, foodborne diseases (FBDs) result in millions of sicknesses and deaths annually. Cumulative evidence suggests that the use of probiotic lactic acid bacteria (LAB) strains could be a viable alternative in inhibiting the activities of foodborne pathogens. This study aims to evaluate the in vitro antimicrobial, cytotoxic, and tolerance levels of Lactobacillus bulgaricus KLDS 1.0207 against two notable foodborne pathogens - Escherichia coli ATCC25922 and Staphylococcus aureus ATCC25923. Afterward, a 48 BALB/c mice-trial was used to assess its ameliorative effects on weight and serum biochemical parameters. Results showed that the cell-free supernatant (CFS) of this strain significantly inhibited both pathogens, but these effects were abolished at pH 6.5 and 7.0 (P < 0.05). Also, 6.96 ± 0.02 log CFU mL-1 of L. bulgaricus KLDS 1.0207 was still viable after three hours in simulated gastric juice and at pH 3.0, indicating that this strain was a potential probiotic candidate. Also, inflammatory activities in RAW264.7 cells were significantly inhibited using 109 CFU mL-1 of L. bulgaricus KLDS 1.0207 cells (P < 0.05). Significant weight losses were also prevented in the T LBSA (from 19.42 ± 1.04 to 19.55 ± 0.55 g) and T LBEC (from 22.86 ± 0.90 to 14.77 ± 9.86 g) groups compared to their respective model groups (T SA - from 21.65 ± 1.80 to 20.14 ± 1.84, and T EC - from 21.45 ± 0.82 to 14.45 ± 9.70 g). Besides, there was a slight weight gain in the S. aureus prevention group (T LBSA ) compared to the model group (T SA ). Serum biochemical analyses revealed that the total cholesterol (TC), triglycerides (TG), low-density lipoprotein (LDL), and some mineral levels were markedly increased by S. aureus and E. coli administrations but were reversed to normalcy in both prevention groups (T LBSA and T LBEC ). Interestingly, high-density lipoprotein (HDL) levels, which were initially disrupted in the model groups, were restored in the prevention groups (T LBSA and T LBEC ). This study presents L. bulgaricus KLDS 1.0207 as a promising probiotic candidate with antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, acid, and bile tolerant and lipid-regulating applications. It also gives valuable insights for targeted future in vivo treatment and prevention studies involving other probiotic LAB candidates. Future in vivo studies elucidating specific mechanisms behind the in vitro antimicrobial, cytotoxic, and in vivo ameliorative effects are warranted.
Keywords: HDL; L. bulgaricus; LDL; anti-inflammation; biochemical; probiotics; tolerance; weight.
Copyright © 2020 Evivie, Abdelazez, Li, Lu, Liu and Huo.
Figures


References
-
- Aboderin F. I., Oyetayo V. O. (2006). Haematological studies of rats fed different doses of probiotic, Lactobacillus plantarum, isolated from fermenting corn slurry. Pakistan J. Nutr. 5 102–105.
-
- Ashraf R., Smith S. C. (2016). Commercial lactic acid bacteria and probiotic strains-tolerance to bile, pepsin and antibiotics. Int. Food Res. J. 23 777–789.
-
- Aziza A. E., Abdelhamid F. M., Risha E. F., Elsayed M. M., Awadin W. F. (2019). Influence of Nigella sativa and rosemary oils on growth performance, biochemical, antioxidant and immunological parameters, and pathological changes in Japanese quail challenged with Escherichia coli. J. Anim. Feed Sci. 28 354–366.
-
- Baroutkoub A., Roushanzamir M., Beglarian R., Julayi H., Sohrabi Z., Mazloomi M., et al. (2010). Effects of probiotic yoghurt consumption on the serum cholesterol levels in hypercholestromic cases in Shiraz, Southern Iran. Sci. Res. Essays 5:2206e9.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

