Prokineticin Receptor Inhibition With PC1 Protects Mouse Primary Sensory Neurons From Neurotoxic Effects of Chemotherapeutic Drugs in vitro
- PMID: 33072073
- PMCID: PMC7541916
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.02119
Prokineticin Receptor Inhibition With PC1 Protects Mouse Primary Sensory Neurons From Neurotoxic Effects of Chemotherapeutic Drugs in vitro
Abstract
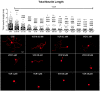
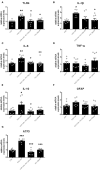
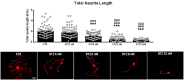
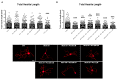
Neurotoxicity is a common side effect of chemotherapeutics that often leads to the development of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN). The peptide Prokineticin 2 (PK2) has a key role in experimental models of CIPN and can be considered an insult-inducible endangering mediator. Since primary afferent sensory neurons are highly sensitive to anticancer drugs, giving rise to dysesthesias, the aim of our study was to evaluate the alterations induced by vincristine (VCR) and bortezomib (BTZ) exposure in sensory neuron cultures and the possible preventive effect of blocking PK2 signaling. Both VCR and BTZ induced a concentration-dependent reduction of total neurite length that was prevented by the PK receptor antagonist PC1. Antagonizing the PK system also reduced the upregulation of PK2, PK-R1, TLR4, IL-6, and IL-10 expression induced by chemotherapeutic drugs. In conclusion, inhibition of PK signaling with PC1 prevented the neurotoxic effects of chemotherapeutics, suggesting a promising strategy for neuroprotective therapies against the sensory neuron damage induced by exposure to these drugs.
Keywords: DRG; chemotherapy; neurons; neurotoxicity; prokineticins.
Copyright © 2020 Moschetti, Kalpachidou, Amodeo, Lattanzi, Sacerdote, Kress and Franchi.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

