Human Chondrocyte Activation by Toxins From Premolis semirufa, an Amazon Rainforest Moth Caterpillar: Identifying an Osteoarthritis Signature
- PMID: 33072083
- PMCID: PMC7531038
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.02191
Human Chondrocyte Activation by Toxins From Premolis semirufa, an Amazon Rainforest Moth Caterpillar: Identifying an Osteoarthritis Signature
Abstract
Pararamosis is a disease that occurs due to contact with the hairs of the larval stage of the Brazilian moth Premolis semirufa. Envenomation induces osteoarticular alterations with cartilage impairment that resembles joint synovitis. Thus, the toxic venom present in the caterpillar hairs interferes with the phenotype of the cells present in the joints, resulting in inflammation and promoting tissue injury. Therefore, to address the inflammatory mechanisms triggered by envenomation, we studied the effects of P. semirufa hair extract on human chondrocytes. We have selected for the investigation, cytokines, chemokines, matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), complement components, eicosanoids, and extracellular matrix (ECM) components related to OA and RA. In addition, for measuring protein-coding mRNAs of some molecules associated with osteoarthritis (OA) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA), reverse transcription (RT) was performed followed by quantitative real-time PCR (RT-qPCR) and we performed the RNA-sequencing (RNA-seq) analysis of the chondrocytes transcriptome. In the supernatant of cell cultures treated with the extract, we observed increased IL-6, IL-8, MCP-1, prostaglandin E2, metalloproteinases (MMP-1, MMP-2, MMP-3 and MMP-13), and complement system components (C3, C4, and C5). We noticed a significant decrease in both aggrecan and type II collagen and an increase in HMGB1 protein in chondrocytes after extract treatment. RNA-seq analysis of the chondrocyte transcriptome allowed us to identify important pathways related to the inflammatory process of the disease, such as the inflammatory response, chemotaxis of immune cells and extracellular matrix (ECM) remodeling. Thus, these results suggest that components of Premolis semirufa hair have strong inflammatory potential and are able to induce cartilage degradation and ECM remodeling, promoting a disease with an osteoarthritis signature. Modulation of the signaling pathways that were identified as being involved in this pathology may be a promising approach to develop new therapeutic strategies for the control of pararamosis and other inflammatory joint diseases.
Keywords: caterpillar; cell signaling; chondrocyte; mediators; osteoarthritis; toxins.
Copyright © 2020 Villas-Boas, Pidde, Lichtenstein, Ching, Junqueira-de-Azevedo, DeOcesano-Pereira, Madureira Trufen, Chudzinski-Tavassi, Morais and Tambourgi.
Figures

 , IL-1β [-x-], 15 μg/mL
, IL-1β [-x-], 15 μg/mL  or 60 μg/mL
or 60 μg/mL  pararama hair extract for 24, 48, and 72 h by centrifugation at 400 ×g at 4°C for 20 min to assess the concentration of cytokines, chemokines, and eicosanoids. The results represent two separate experiments performed in duplicate and are expressed as the mean of the concentrations of the molecules ± SEM. The data were analyzed using two-way ANOVA and Dunnett's post hoc test. **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001 vs. the control (buffer treatment).
pararama hair extract for 24, 48, and 72 h by centrifugation at 400 ×g at 4°C for 20 min to assess the concentration of cytokines, chemokines, and eicosanoids. The results represent two separate experiments performed in duplicate and are expressed as the mean of the concentrations of the molecules ± SEM. The data were analyzed using two-way ANOVA and Dunnett's post hoc test. **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001 vs. the control (buffer treatment).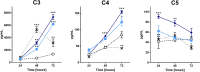
 , IL-1β [-x-], 15 μg/mL
, IL-1β [-x-], 15 μg/mL  or 60 μg/mL
or 60 μg/mL  pararama hair extract for 24, 48, and 72 h. After each treatment period, we removed the supernatants, centrifuged them at 400 ×g at 4°C for 20 min, and assessed the concentrations of complement components by ELISA. The results represent two separate experiments performed in duplicate and are expressed as the mean of the concentrations of the complement components ± SEM. The data were analyzed using two-way ANOVA and Dunnett's post hoc test. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001 vs. the control (buffer treatment).
pararama hair extract for 24, 48, and 72 h. After each treatment period, we removed the supernatants, centrifuged them at 400 ×g at 4°C for 20 min, and assessed the concentrations of complement components by ELISA. The results represent two separate experiments performed in duplicate and are expressed as the mean of the concentrations of the complement components ± SEM. The data were analyzed using two-way ANOVA and Dunnett's post hoc test. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001 vs. the control (buffer treatment).
 , IL-1β [-x-], 15 μg/mL
, IL-1β [-x-], 15 μg/mL  or 60 μg/mL
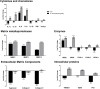
or 60 μg/mL  pararama hair extract for 24, 48, and 72 h. After each treatment period, we removed the supernatants, centrifuged them at 400 ×g at 4°C for 20 min, and assessed the concentration of matrix metalloproteinases by ELISA. The results represent two separate experiments performed in duplicate and are expressed as the mean of the concentrations of the metalloproteinases ± SEM. The data were analyzed using two-way ANOVA and Dunnett's post hoc test. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001 vs. the control (buffer treatment).
pararama hair extract for 24, 48, and 72 h. After each treatment period, we removed the supernatants, centrifuged them at 400 ×g at 4°C for 20 min, and assessed the concentration of matrix metalloproteinases by ELISA. The results represent two separate experiments performed in duplicate and are expressed as the mean of the concentrations of the metalloproteinases ± SEM. The data were analyzed using two-way ANOVA and Dunnett's post hoc test. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001 vs. the control (buffer treatment).

References
-
- Rodrigues MG. Efeitos danosos da lagarta “Pararama”. (Premolis semirufa) a seringueiros no Estado do Pará. Bol FCAP. (1976) 8:1–31.
-
- Dias LB, Azevedo MC. Pararama: doença dos seringais. In: Veronesi R. editor. Doenças Infecciosas e Parasitárias. Rio de Janeiro: Guanabara Koogan; (1991). p. 988–9.
-
- Costa RM, Silva NP, Teves DC, Costa ML, Ferraz MB AE. Experimental arthritis induced by bristles from a “Lepidoptera”, “Premolis semirufa”: histopathological study in rats. Rev Bras Reumatol. (1995) 35:61–4.
-
- Costa RM. Pararamosis: uma reumatose ocupacional. Rev Bras Reumatol. (1981) 21:132–6.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

