Adenovirus 7 Induces Interlukin-6 Expression in Human Airway Epithelial Cells via p38/NF-κB Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 33072092
- PMCID: PMC7538593
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.551413
Adenovirus 7 Induces Interlukin-6 Expression in Human Airway Epithelial Cells via p38/NF-κB Signaling Pathway
Abstract
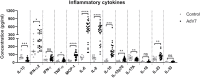
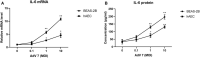
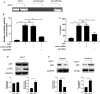
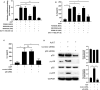
Human Adenovirus (AdV) infection is very common and usually has a significant impact on children. AdV-induced inflammation is believed to be one of the main causes of severe symptoms. However, an inflammatory response profile in the airway in AdV-infected children is still lacking, and the mechanism underlying AdV-induced inflammation in the airway is also poorly understood. In the current study, we determined the expression of a panel of inflammation cytokines in the airway samples from AdV 7 infected children and further investigated the molecular mechanism underlying AdV 7-induced cytokine expression. Our results showed that eight out of 13 tested inflammatory cytokines were significantly increased in nasal washes of AdV 7-infected children comparing to healthy control, with IL-6 showing the highest enhancement. AdV 7 infection of bronchial epithelial cell line and primary airway epithelial cells confirmed that AdV 7 increased IL-6 mRNA and protein expression in an infection dose-dependent manner. Promoter analysis revealed that AdV 7 infection transactivated IL-6 promoter and a NF-κB binding site in IL-6 promoter was involved in the transactivation. Further analysis showed that upon AdV 7 infection, NF-κB p65 was phosphorylated and translocated into nucleus and bound onto IL-6 promoter. Signaling pathway analysis revealed that p38/NF-κB pathway was involved in AdV 7 infection induced IL-6 elevation. Taken together, our study shows that AdV 7 infection triggers the expression of a range of inflammatory cytokines including IL-6 in the airway of infected children, and AdV 7 enhances IL-6 expression by transactivating IL-6 promoter via p38/NF-κB signaling pathway. Findings of our current study have provided more information toward a better understanding of AdV-induced airway inflammation, which might also benefit the development of intervention strategies.
Keywords: Adenovirus 7; Interlukin-6; airway epithelial cell; inflammation; p38/NF-κB signaling pathway.
Copyright © 2020 Qi, Wang, Wang and Deng.
Figures

References
-
- Chuang Y, Chiu C-H, Wong K-S, Huang J-G, Huang YC, Chang LY, et al. . Severe adenovirus infection in children. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. (2003) 36:37–40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

