Safety and immunogenicity evaluation of recombinant BCG vaccine against respiratory syncytial virus in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase I clinical trial
- PMID: 33073219
- PMCID: PMC7548429
- DOI: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100517
Safety and immunogenicity evaluation of recombinant BCG vaccine against respiratory syncytial virus in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase I clinical trial
Abstract
Background: Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is responsible for most respiratory tract infections and hospitalizations in infants and represents a significant economic burden for public health. The development of a safe, effective, and affordable vaccine is a priority for the WHO.
Methods: We conducted a double-blinded, escalating-dose phase 1 clinical trial in healthy males aged 18-50 years to evaluate safety, tolerability, and immunogenicity of a recombinant Mycobacterium bovis BCG vaccine expressing the nucleoprotein of RSV (rBCG-N-hRSV). Once inclusion criteria were met, volunteers were enrolled in three cohorts in an open and successive design. Each cohort included six volunteers vaccinated with 5 × 103, 5 × 104, or 1 × 105 CFU, as well as two volunteers vaccinated with the full dose of the standard BCG vaccine. This clinical trial (clinicaltrials.gov NCT03213405) was conducted in Santiago, Chile.
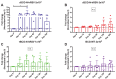
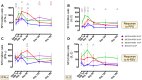
Findings: The rBCG-N-RSV vaccine was safe, well-tolerated, and no serious adverse events related to the vaccine were recorded. Serum IgG-antibodies directed against Mycobacterium and the N-protein of RSV increased after vaccination, which were capable of neutralizing RSV in vitro. Additionally, all volunteers displayed increased cellular response consisting of IFN-γ and IL-2 production against PPD and the N-protein, starting at day 14 and 30 post-vaccination respectively.
Interpretation: The rBCG-N-hRSV vaccine had a good safety profile and induced specific cellular and humoral responses.
Funding: This work was supported by Millennium Institute on Immunology and Immunotherapy from Chile (P09/016), FONDECYT 1190830, and FONDEF D11E1098.
Keywords: BCG vaccine; Human respiratory syncytial virus; Immunogenicity; Phase I clinical trial; Safety; Transmissibility.
© 2020 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors KA, ERJ, NMD, YV, JS, NG, JV, CI, MU, AB, JC, VM, PG, JG, SB, and AMK report grants from Millennium Institute on Immunology and Immunotherapy from Chile, grants from Fondo Nacional de Desarrollo Científico y Tecnológico, grants from Fondo de Fomento al Desarrollo Tecnológico, personal fees from Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile, during the conduct of the study. LV reports personal fees from Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile, during the conduct of the study .
Figures


References
-
- Breese Hall C. The burgeoning burden of respiratory syncytial virus among children. Infect Disord – Drug Targets. 2012;12:92–97. - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

