Amino acid synthesis loss in parasitoid wasps and other hymenopterans
- PMID: 33074103
- PMCID: PMC7593089
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.59795
Amino acid synthesis loss in parasitoid wasps and other hymenopterans
Retraction in
-
Retraction: Amino acid synthesis loss in parasitoid wasps and other hymenopterans.Elife. 2020 Dec 1;9:e65123. doi: 10.7554/eLife.65123. Elife. 2020. PMID: 33258773 Free PMC article.
Abstract
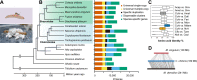
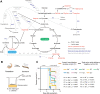
Insects utilize diverse food resources which can affect the evolution of their genomic repertoire, including leading to gene losses in different nutrient pathways. Here, we investigate gene loss in amino acid synthesis pathways, with special attention to hymenopterans and parasitoid wasps. Using comparative genomics, we find that synthesis capability for tryptophan, phenylalanine, tyrosine, and histidine was lost in holometabolous insects prior to hymenopteran divergence, while valine, leucine, and isoleucine were lost in the common ancestor of Hymenoptera. Subsequently, multiple loss events of lysine synthesis occurred independently in the Parasitoida and Aculeata. Experiments in the parasitoid Cotesia chilonis confirm that it has lost the ability to synthesize eight amino acids. Our findings provide insights into amino acid synthesis evolution, and specifically can be used to inform the design of parasitoid artificial diets for pest control.
Keywords: Cotesia chilonis; amino acid synthesis; comparative genomics; genetics; genome sequencing; genomics; parasitoid wasps; trait loss.
© 2020, Ye et al.
Conflict of interest statement
XY, SX, ZT, YY, JW, KY, HW, YM, ZY, SC, CY, FW, HY, QF, QS, JW, GY, FL No competing interests declared
Figures








References
-
- Bank S, Sann M, Mayer C, Meusemann K, Donath A, Podsiadlowski L, Kozlov A, Petersen M, Krogmann L, Meier R, Rosa P, Schmitt T, Wurdack M, Liu S, Zhou X, Misof B, Peters RS, Niehuis O. Transcriptome and target DNA enrichment sequence data provide new insights into the phylogeny of vespid wasps (Hymenoptera: aculeata: vespidae) Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution. 2017;116:213–226. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2017.08.020. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
- Major International (Regional) Joint Research Project of NSFC,31620103915/National Natural Science Foundation of China/International
- Key Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China,31830074/National Natural Science Foundation of China/International
- 31772238/National Natural Science Foundation of China/International
- 2017YFD0200400/National Key Research and Development Program of China/International
- 2017YFD0200904/National Key Research and Development Program of China/International
- IOS-1456233/National Science Foundation/International
- Major International (Regional) Joint Research Project of National Natural Science Foundation of China 31620103915/National Natural Science Foundation of China/International
- Key Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China 31830074/National Natural Science Foundation of China/International
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

