Impaired Myocardial Energetics Causes Mechanical Dysfunction in Decompensated Failing Hearts
- PMID: 33074265
- PMCID: PMC7552914
- DOI: 10.1093/function/zqaa018
Impaired Myocardial Energetics Causes Mechanical Dysfunction in Decompensated Failing Hearts
Abstract
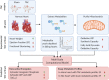
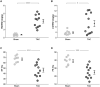
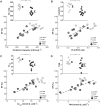
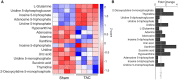
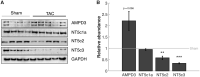
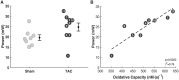
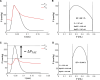
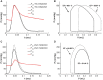
Cardiac mechanical function is supported by ATP hydrolysis, which provides the chemical-free energy to drive the molecular processes underlying cardiac pumping. Physiological rates of myocardial ATP consumption require the heart to resynthesize its entire ATP pool several times per minute. In the failing heart, cardiomyocyte metabolic dysfunction leads to a reduction in the capacity for ATP synthesis and associated free energy to drive cellular processes. Yet it remains unclear if and how metabolic/energetic dysfunction that occurs during heart failure affects mechanical function of the heart. We hypothesize that changes in phosphate metabolite concentrations (ATP, ADP, inorganic phosphate) that are associated with decompensation and failure have direct roles in impeding contractile function of the myocardium in heart failure, contributing to the whole-body phenotype. To test this hypothesis, a transverse aortic constriction (TAC) rat model of pressure overload, hypertrophy, and decompensation was used to assess relationships between metrics of whole-organ pump function and myocardial energetic state. A multiscale computational model of cardiac mechanoenergetic coupling was used to identify and quantify the contribution of metabolic dysfunction to observed mechanical dysfunction. Results show an overall reduction in capacity for oxidative ATP synthesis fueled by either fatty acid or carbohydrate substrates as well as a reduction in total levels of adenine nucleotides and creatine in myocardium from TAC animals compared to sham-operated controls. Changes in phosphate metabolite levels in the TAC rats are correlated with impaired mechanical function, consistent with the overall hypothesis. Furthermore, computational analysis of myocardial metabolism and contractile dynamics predicts that increased levels of inorganic phosphate in TAC compared to control animals kinetically impair the myosin ATPase crossbridge cycle in decompensated hypertrophy/heart failure.
Keywords: cardiac energetics; cardiomyopathy; computational modeling; ejection fraction; heart failure; mechanoenergetic coupling; mitochondria; oxidative respiration; transaortic constriction.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of American Physiological Society.
Figures


Comment in
-
Computational/Experimental Interrogation of the Failing Heart-A Perspective on "Impaired Myocardial Energetics Causes Mechanical Dysfunction in Decompensated Failing Hearts".Function (Oxf). 2020 Oct 9;1(2):zqaa022. doi: 10.1093/function/zqaa022. eCollection 2020. Function (Oxf). 2020. PMID: 35330639 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Lassers BW, Kaijser L, Wahlqvist ML, et al.Relationship in man between plasma free fatty acids and myocardial metabolism of carbohydrate substrates. Lancet 1971;2(7722):448–450. - PubMed
-
- Liepinsh E, Makrecka M, Kuka J, et al. The heart is better protected against myocardial infarction in the fed state compared to the fasted state. Metabolism 2014;63(1):127–136. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
