Efficacy and safety of once-weekly semaglutide versus once-daily sitagliptin as add-on to metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes in SUSTAIN China: A 30-week, double-blind, phase 3a, randomized trial
- PMID: 33074557
- PMCID: PMC7839591
- DOI: 10.1111/dom.14232
Efficacy and safety of once-weekly semaglutide versus once-daily sitagliptin as add-on to metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes in SUSTAIN China: A 30-week, double-blind, phase 3a, randomized trial
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate the efficacy and safety of once-weekly subcutaneous semaglutide, a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) analogue, versus once-daily sitagliptin as add-on to metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D) in a multiregional clinical trial.
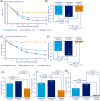
Materials and methods: In the 30-week, randomized, double-blind, double-dummy, active comparator SUSTAIN China trial, 868 adults with T2D inadequately controlled on metformin (HbA1c 7.0%-10.5%) were randomized to receive once-weekly semaglutide 0.5 mg (n = 288), semaglutide 1.0 mg (n = 290) or once-daily sitagliptin 100 mg (n = 290). The primary and confirmatory secondary endpoints were change from baseline to week 30 in HbA1c and body weight, respectively.
Results: The trial enrolled ~70% (605/868) of the patients in China, and the remaining patients from four other countries, including the Republic of Korea. Both doses of semaglutide were superior to sitagliptin in reducing HbA1c and body weight after 30 weeks of treatment. The odds of achieving target HbA1c of less than 7.0% (53 mmol/mol), weight loss of 5% or higher, or 10% or higher, and the composite endpoint of HbA1c less than 7.0% (53 mmol/mol) without severe or blood glucose-confirmed symptomatic hypoglycaemia no weight gain, were all significantly higher with both semaglutide doses compared with sitagliptin. The safety profile for semaglutide was consistent with the known class effects of GLP-1 receptor agonists (RAs). Consistent efficacy and safety findings were seen in the Chinese subpopulation.
Conclusions: Once-weekly semaglutide was superior to sitagliptin in improving glycaemic control and reducing body weight in patients with T2D inadequately controlled on metformin. The safety and tolerability profiles were consistent with those of semaglutide and other GLP-1 RAs. Semaglutide is an effective once-weekly treatment option for the Chinese population.
Keywords: GLP-1 analogue, glycaemic control, incretin therapy, phase III study, randomized trial, type 2 diabetes.
© 2020 The Authors. Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
LJ reports receiving personal fees from Novo Nordisk during the conduct of this study. ZN is an employee of Novo Nordisk. SR is an employee of and stockholder at Novo Nordisk. TVS is an employee of and shareholder at Novo Nordisk. XD, YiL, YuL, SL, ML and GY have nothing to disclose. FGE reports receiving grants from Novo Nordisk outside the submitted work.
Figures

References
-
- International Diabetes Federation . IDF Diabetes Atlas. 9th ed. Brussels, Belgium; 2019.
-
- Turner RC, Holman RR, Stratton IM, et al. Effect of intensive blood‐glucose control with metformin on complications in overweight patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 34). Lancet. 1998;352(9131):854‐865. - PubMed
-
- UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group . Effect of intensive blood‐glucose control with metformin on complications in overweight patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 34). Lancet. 1998;352(9131):854‐865. - PubMed
-
- UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group . Intensive blood‐glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). Lancet. 1998;352(9131):837‐853. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

