Management of Irrational Self-Purchase of Hydroxychloroquine During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Experiences From the Largest Healthcare System in Taiwan
- PMID: 33074933
- PMCID: PMC7787064
- DOI: 10.1097/PTS.0000000000000795
Management of Irrational Self-Purchase of Hydroxychloroquine During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Experiences From the Largest Healthcare System in Taiwan
Conflict of interest statement
The authors disclose no conflict of interest.
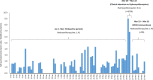
Figures
Comment on
-
RETRACTED: Hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin as a treatment of COVID-19: results of an open-label non-randomized clinical trial.Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2020 Jul;56(1):105949. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105949. Epub 2020 Mar 20. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2020. Retraction in: Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2025 Jan;65(1):107416. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2024.107416. PMID: 32205204 Free PMC article. Retracted. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Sanders JM Monogue ML Jodlowski TZ, et al. Pharmacologic treatments for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a review. JAMA. 2020;323:1824–1836. - PubMed
-
- Shao SC Chan YY Kao Yang YH, et al. The Chang gung research database-a multi-institutional electronic medical records database for real-world epidemiological studies in Taiwan. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2019;28:593–600. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical