Cytokine elevation in severe and critical COVID-19: a rapid systematic review, meta-analysis, and comparison with other inflammatory syndromes
- PMID: 33075298
- PMCID: PMC7567529
- DOI: 10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30404-5
Cytokine elevation in severe and critical COVID-19: a rapid systematic review, meta-analysis, and comparison with other inflammatory syndromes
Abstract
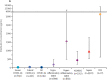
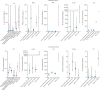
The description of a so-called cytokine storm in patients with COVID-19 has prompted consideration of anti-cytokine therapies, particularly interleukin-6 antagonists. However, direct systematic comparisons of COVID-19 with other critical illnesses associated with elevated cytokine concentrations have not been reported. In this Rapid Review, we report the results of a systematic review and meta-analysis of COVID-19 studies published or posted as preprints between Nov 1, 2019, and April 14, 2020, in which interleukin-6 concentrations in patients with severe or critical disease were recorded. 25 COVID-19 studies (n=1245 patients) were ultimately included. Comparator groups included four trials each in sepsis (n=5320), cytokine release syndrome (n=72), and acute respiratory distress syndrome unrelated to COVID-19 (n=2767). In patients with severe or critical COVID-19, the pooled mean serum interleukin-6 concentration was 36·7 pg/mL (95% CI 21·6-62·3 pg/mL; I2=57·7%). Mean interleukin-6 concentrations were nearly 100 times higher in patients with cytokine release syndrome (3110·5 pg/mL, 632·3-15 302·9 pg/mL; p<0·0001), 27 times higher in patients with sepsis (983·6 pg/mL, 550·1-1758·4 pg/mL; p<0·0001), and 12 times higher in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome unrelated to COVID-19 (460 pg/mL, 216·3-978·7 pg/mL; p<0·0001). Our findings question the role of a cytokine storm in COVID-19-induced organ dysfunction. Many questions remain about the immune features of COVID-19 and the potential role of anti-cytokine and immune-modulating treatments in patients with the disease.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


Comment in
-
Assessing the importance of interleukin-6 in COVID-19 - Authors' reply.Lancet Respir Med. 2021 Feb;9(2):e14-e15. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30603-2. Epub 2021 Jan 15. Lancet Respir Med. 2021. PMID: 33460572 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Moore JB, June CH. Cytokine release syndrome in severe COVID-19. Science. 2020;368:473–474. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

