Deferred Administration of Afobazole Induces Sigma1R-Dependent Restoration of Striatal Dopamine Content in a Mouse Model of Parkinson's Disease
- PMID: 33076300
- PMCID: PMC7593947
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21207620
Deferred Administration of Afobazole Induces Sigma1R-Dependent Restoration of Striatal Dopamine Content in a Mouse Model of Parkinson's Disease
Abstract
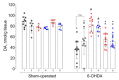
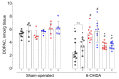
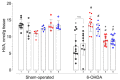
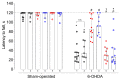
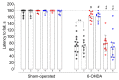
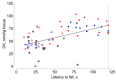
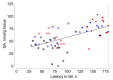
Previously, we demonstrated that the immediate administration of multitarget anxiolytic afobazole slows down the progression of neuronal damage in a 6-hydroxidodamine (6-OHDA) model of Parkinson's disease due to the activation of chaperone Sigma1R. The aim of the present study is to evaluate the therapeutic potential of deferred afobazole administration in this model. Male ICR mice received a unilateral 6-OHDA lesion of the striatum. Fourteen days after the surgery, mice were treated with afobazole, selective Sigma1R agonist PRE-084, selective Sigma1R antagonist BD-1047, and a combination of BD-1047 with afobazole or PRE-084 for another 14 days. The deferred administration of afobazole restored the intrastriatal dopamine content in the 6-OHDA-lesioned striatum and facilitated motor behavior in rotarod tests. The action of afobazole accorded with the effect of Sigma1R selective agonist PRE-084 and was blocked by Sigma1R selective antagonist BD-1047. The present study illustrates the Sigma1R-dependent effects of afobazole in a 6-OHDA model of Parkinson's disease and reveals the therapeutic potential of Sigma1R agonists in treatment of the condition.
Keywords: 6-OHDA; BD-1047; PRE-084; Parkinson’s disease; afobazole; chaperone Sigma1R; dopamine; rotarod; tyrosine hydroxylase.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Involvement of Chaperone Sigma1R in the Anxiolytic Effect of Fabomotizole.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 21;22(11):5455. doi: 10.3390/ijms22115455. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34064275 Free PMC article.
-
Chaperone Sigma1R mediates the neuroprotective action of afobazole in the 6-OHDA model of Parkinson's disease.Sci Rep. 2019 Nov 19;9(1):17020. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-53413-w. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31745133 Free PMC article.
-
Afobazole modulates neuronal response to ischemia and acidosis via activation of sigma-1 receptors.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2011 Oct;339(1):152-60. doi: 10.1124/jpet.111.182774. Epub 2011 Jun 29. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2011. PMID: 21715562
-
The sigma-1 receptor as a regulator of dopamine neurotransmission: A potential therapeutic target for methamphetamine addiction.Pharmacol Ther. 2018 Jun;186:152-167. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2018.01.009. Epub 2018 Jan 31. Pharmacol Ther. 2018. PMID: 29360540 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In vitro and in vivo sigma 1 receptor imaging studies in different disease states.RSC Med Chem. 2020 Oct 8;12(2):154-177. doi: 10.1039/d0md00186d. eCollection 2021 Mar 4. RSC Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 34046607 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting Sigma-1 Receptor: A Promising Strategy in the Treatment of Parkinson's Disease.Neurochem Res. 2023 Oct;48(10):2925-2935. doi: 10.1007/s11064-023-03960-6. Epub 2023 May 31. Neurochem Res. 2023. PMID: 37259012 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Involvement of Chaperone Sigma1R in the Anxiolytic Effect of Fabomotizole.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 21;22(11):5455. doi: 10.3390/ijms22115455. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34064275 Free PMC article.
-
Sigma-1 Receptor: A Potential Therapeutic Target for Traumatic Brain Injury.Front Cell Neurosci. 2021 Sep 30;15:685201. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2021.685201. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34658788 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chaperone-Dependent Mechanisms as a Pharmacological Target for Neuroprotection.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 3;24(1):823. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010823. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36614266 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors in Toxic Models of Parkinsonism.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jan 31;26(3):1248. doi: 10.3390/ijms26031248. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39941014 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

