The combined antibacterial effects of sodium new houttuyfonate and berberine chloride against growing and persistent methicillin-resistant and vancomycin-intermediate Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 33076836
- PMCID: PMC7574187
- DOI: 10.1186/s12866-020-02003-2
The combined antibacterial effects of sodium new houttuyfonate and berberine chloride against growing and persistent methicillin-resistant and vancomycin-intermediate Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
Background: Infections caused by drug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, especially vancomycin-intermediate Staphylococcus aureus (VISA), leave clinicians with limited therapeutic options for treatment. Persister cells is a leading cause of recalcitrant infection and antibiotic treatment failure, and there is no drug in clinical use that specifically targets persister cells currently. Here, we report a promising combination therapy of sodium new houttuyfonate (SNH) and berberine chloride (BBR) which is able to eradicate both growing and persistent drug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.
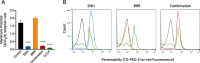
Results: The susceptibility test showed SNH exhibited anti-MRSA activity with MIC90 at 64 μg/mL, while BBR showed weak anti-MRSA activity with MIC90 at 512 μg/mL. MICs of BBR in combination with 1/2 MIC SNH decreased by 4 to 64 folds compared with MICs of BBR alone. The results of time-killing assays revealed that the combined use of sub-MIC SNH and BBR offered an in vitro synergistic action against growing MRSA (including pathogenic MRSA) and VISA strains. More importantly, the combination of SNH and BBR was able to eradicate VISA Mu50 and pathogenic MRSA persister cells. The synergistic effect is likely related to the interruption of the cell membrane caused by SNH, which is confirmed by scanning electron microscope and membrane potential and permeability analysis.
Conclusions: Our study provide a promising clinical curative strategy for combating drug-resistant S. aureus infections, especially for recalcitrant infections caused by persister cells.
Keywords: Berberine; Combination therapy; MRSA; Persistence; Sodium new houttuyfonate; VISA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

