Risk conditions in children hospitalized with influenza in Norway, 2017-2019
- PMID: 33076855
- PMCID: PMC7569759
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-020-05486-6
Risk conditions in children hospitalized with influenza in Norway, 2017-2019
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Risk conditions in children hospitalized with influenza in Norway, 2017-2019.BMC Infect Dis. 2021 Feb 22;21(1):197. doi: 10.1186/s12879-021-05913-2. BMC Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 33618654 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Norwegian children are more frequently hospitalized with influenza than adults. Little is known about the characteristics of these children. Our aim was to investigate the presence of pre-existing risk conditions and to determine the duration of influenza hospitalizations in children during two influenza seasons.
Methods: The Norwegian Patient Registry holds data on all hospitalized patients in Norway. We included all patients younger than 18 years hospitalized with a diagnosis of influenza during the influenza seasons 2017-18 and 2018-19. Pre-existing risk conditions for influenza were identified by ICD-10 diagnoses in the Norwegian Patient Registry. In addition, information on asthma diagnoses were also retrieved from the Norwegian Registry for Primary Health Care. To estimate the prevalence of risk conditions in the child population, we obtained diagnoses on all Norwegian children in a two-year period prior to each influenza season. We calculated age-specific rates for hospitalization and risk for being hospitalized with influenza in children with risk conditions.
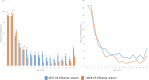
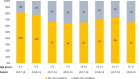
Results: In total, 1013 children were hospitalized with influenza during the two influenza seasons. Children younger than 6 months had the highest rate of hospitalization, accounting for 13.5% of all admissions (137 children). Hospitalization rates decreased with increasing age. Among children hospitalized with influenza, 25% had one or more pre-existing risk conditions for severe influenza, compared to 5% in the general population under 18 years. Having one or more risk conditions significantly increased the risk of hospitalization, (Odds Ratio (OR) 6.1, 95% confidence interval (CI) 5.0-7.4 in the 2017-18 season, and OR 6.8, 95% CI 5.4-8.4 in the 2018-19 season). Immunocompromised children and children with epilepsy had the highest risk of hospitalization with influenza, followed by children with heart disease and lung disease. The average length of stay in hospital were 4.6 days, and this did not differ with age.
Conclusion: Children with pre-existing risk conditions for influenza had a higher risk of hospitalization for influenza. However, most children (75%) admitted to hospital with influenza in Norway during 2017-2019 did not have pre-existing risk conditions. Influenza vaccination should be promoted in particular for children with risk conditions and pregnant women to protect new-borns.
Keywords: Children; Hospitalizations; Influenza; Risk conditions; Vaccination.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Nair H, Simoes EA, Rudan I, Gessner BD, Azziz-Baumgartner E, Zhang JSF, et al. Global and regional burden of hospital admissions for severe acute lower respiratory infections in young children in 2010: a systematic analysis. Lancet. 2013;381(9875):1380–1390. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61901-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

