The use of venous Doppler to predict adverse kidney events in a general ICU cohort
- PMID: 33076961
- PMCID: PMC7574322
- DOI: 10.1186/s13054-020-03330-6
The use of venous Doppler to predict adverse kidney events in a general ICU cohort
Abstract
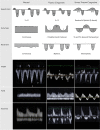
Background: Changes in Doppler flow patterns of hepatic veins (HV), portal vein (PV) and intra-renal veins (RV) reflect right atrial pressure and venous congestion; the feasibility of obtaining these assessments and the clinical relevance of the findings is unknown in a general ICU population. This study compares the morphology of HV, PV and RV waveform abnormalities in prediction of major adverse kidney events at 30 days (MAKE30) in critically ill patients.
Study design and methods: We conducted a prospective observational study enrolling adult patients within 24 h of admission to the ICU. Patients underwent an ultrasound evaluation of the HV, PV and RV. We compared the rate of MAKE-30 events in patients with and without venous flow abnormalities in the hepatic, portal and intra-renal veins. The HV was considered abnormal if S to D wave reversal was present. The PV was considered abnormal if the portal pulsatility index (PPI) was greater than 30%. We also examined PPI as a continuous variable to assess whether small changes in portal vein flow was a clinically important marker of venous congestion.
Results: From January 2019 to June 2019, we enrolled 114 patients. HV abnormalities demonstrate an odds ratio of 4.0 (95% CI 1.4-11.2). PV as a dichotomous outcome is associated with an increased odds ratio of MAKE-30 but fails to reach statistical significance (OR 2.3 95% CI 0.87-5.96), but when examined as a continuous variable it demonstrates an odds ratio of 1.03 (95% CI 1.00-1.06). RV Doppler flow abnormalities are not associated with an increase in the rate of MAKE-30 INTERPRETATION: Obtaining hepatic, portal and renal venous Doppler assessments in critically ill ICU patients are feasible. Abnormalities in hepatic and portal venous Doppler are associated with an increase in MAKE-30. Further research is needed to determine if venous Doppler assessments can be useful measures in assessing right-sided venous congestion in critically ill patients.
Keywords: Ultrasound; Venous congestion; Venous return.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical