A brain network that supports consensus-seeking and conflict-resolving of college couples' shopping interaction
- PMID: 33077801
- PMCID: PMC7573624
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-74699-1
A brain network that supports consensus-seeking and conflict-resolving of college couples' shopping interaction
Abstract
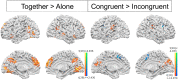
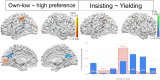
One of the typical campus scenes is the social interaction between college couples, and the lesson couples must keep learning is to adapt to each other. This fMRI study investigated the shopping interactions of 30 college couples, one lying inside and the other outside the scanner, beholding the same item from two connected PCs, making preference ratings and subsequent buy/not-buy decisions. The behavioral results showed the clear modulation of significant others' preferences onto one's own decisions, and the contrast of the "shop-together vs. shop-alone", and the "congruent (both liked or disliked the item, 68%) vs. incongruent (one liked but the other disliked, and vice versa)" together trials, both revealed bilateral temporal parietal junction (TPJ) among other reward-related regions, likely reflecting mentalizing during preference harmony. Moreover, when contrasting "own-high/other-low vs. own-low/other-high" incongruent trials, left anterior inferior parietal lobule (l-aIPL) was parametrically mapped, and the "yield (e.g., own-high/not-buy) vs. insist (e.g., own-low/not-buy)" modulation further revealed left lateral-IPL (l-lIPL), together with left TPJ forming a local social decision network that was further constrained by the mediation analysis among left TPJ-lIPL-aIPL. In sum, these results exemplify, via the two-person fMRI, the neural substrate of shopping interactions between couples.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Theory-of-mind-related neural activity for one's romantic partner predicts partner well-being.Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2016 Apr;11(4):593-603. doi: 10.1093/scan/nsv144. Epub 2015 Nov 25. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 26609107 Free PMC article.
-
Brain circuits involved in understanding our own and other's internal states in the context of romantic relationships.Soc Neurosci. 2019 Dec;14(6):729-738. doi: 10.1080/17470919.2019.1586758. Epub 2019 Mar 8. Soc Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30806571
-
Spatio-temporal patterns of cognitive control revealed with simultaneous electroencephalography and functional magnetic resonance imaging.Hum Brain Mapp. 2019 Jan;40(1):80-97. doi: 10.1002/hbm.24356. Epub 2018 Sep 26. Hum Brain Mapp. 2019. PMID: 30259592 Free PMC article.
-
The inferior parietal lobule and temporoparietal junction: A network perspective.Neuropsychologia. 2017 Oct;105:70-83. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2017.01.001. Epub 2017 Jan 3. Neuropsychologia. 2017. PMID: 28057458 Review.
-
The Role of the Temporoparietal Junction in Self-Other Distinction.Brain Topogr. 2019 Nov;32(6):943-955. doi: 10.1007/s10548-019-00737-5. Epub 2019 Nov 1. Brain Topogr. 2019. PMID: 31676934 Review.
Cited by
-
Unsupervised skull segmentation in MR images utilizing modality translation and super-resolution.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 16;15(1):25828. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-05323-3. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40670405 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Honkanen P, Verplanken B, Olsen SO. Ethical values and motives driving organic food choice. J. Consumer Behav. 2006;5:420–430. doi: 10.1002/cb.190. - DOI
-
- Cryer D, Burchinal M. Parents as child care consumers. Early Childhood Res. Quart. 1997;12:35–58. doi: 10.1016/S0885-2006(97)90042-9. - DOI
-
- Cavanaugh LA. Consumer behavior in close relationships. Curr. Opin. Psychol. 2016;10:101–106. doi: 10.1016/j.copsyc.2015.11.004. - DOI
-
- Simpson JA, Griskevicius V, Rothman AJ. Consumer decisions in relationships. J. Consumer Psychol. 2012;22:304–314. doi: 10.1016/j.jcps.2011.09.007. - DOI
-
- Hwang JW. Effect of prosocial behaviors in a mating mindset on purchase decisions. Social Behav. Personal. Int. J. 2016;44:463–479. doi: 10.2224/sbp.2016.44.3.463. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

