A materials-science perspective on tackling COVID-19
- PMID: 33078077
- PMCID: PMC7556605
- DOI: 10.1038/s41578-020-00247-y
A materials-science perspective on tackling COVID-19
Abstract
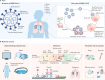
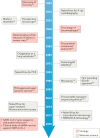
The ongoing SARS-CoV-2 pandemic highlights the importance of materials science in providing tools and technologies for antiviral research and treatment development. In this Review, we discuss previous efforts in materials science in developing imaging systems and microfluidic devices for the in-depth and real-time investigation of viral structures and transmission, as well as material platforms for the detection of viruses and the delivery of antiviral drugs and vaccines. We highlight the contribution of materials science to the manufacturing of personal protective equipment and to the design of simple, accurate and low-cost virus-detection devices. We then investigate future possibilities of materials science in antiviral research and treatment development, examining the role of materials in antiviral-drug design, including the importance of synthetic material platforms for organoids and organs-on-a-chip, in drug delivery and vaccination, and for the production of medical equipment. Materials-science-based technologies not only contribute to the ongoing SARS-CoV-2 research efforts but can also provide platforms and tools for the understanding, protection, detection and treatment of future viral diseases.
Keywords: Diseases; Materials science; Nanoscience and technology; Virology.
© Springer Nature Limited 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsO.C.F. has financial interests in Selecta Biosciences, Tarveda Therapeutics and Seer. R.L. receives licensing fees (to patents on which he was an inventor) from, invested in, consults (or was on scientific advisory boards or boards of directors) for, lectured (and received a fee) or conducts sponsored research at MIT for which he was not paid for the following entities: 7th Sense, Abpro Labs, Abpro Korea, Acorda (formerly Civitas Therapeutics), Aleph Farms, Alivio Therapeutics, Alkermes, Allevi, Alnylam Pharmaceuticals, Apotex, Arcadia Biosciences, Arsenal Medical, Artificial Cells, Avalon GloboCare, BASF, BioInnovation Institute, Blackstone, Boston Children’s Hospital, Celero, Cellomics, Cellular Biomedical, Charles River, Clontech, Combined Therapeutics, Conference Forum, Cornell University, CRISPR Therapeutics AG, Crown Bioscience, Cygnal Therapeutics, Daros, Daré Bioscience, DeepBiome, Dewpoint Therapeutics, Dispendix/Cellink, Domain, Eagle, EdiGene Biotechnology, Editas Medicine, Eli Lily, Eisai, Entrega, Everlywell, Evox Therapeutics, Flagship Pioneering, Frequency Therapeutics, GeneMedicine, GenScript USA, GENUV, GlaxoSmithKline, Glycobia, Glympse Bio, GreenLight Biosciences, HCR, Hopewell Therapeutics, Horizon Discovery, Humacyte, IBEX Pharmaceuticals, ImmuneXcite, Indivior, Inovio, Institute of Immunology, Integrated DNA Technologies, InVivo Therapeutics, IxBio, J.R. Simplot, Jnana Therapeutics, Kala Pharmaceuticals, Kallyope, Kensa, Kodikaz Therapeutics, KSQ Therapeutics, Landsdowne Labs, LikeMinds, Luminopia, Luye, Lyndra Therapeutics, Lyra Therapeutics, McGovern Institute, Medikinetics, Merck, MGH Ragon Institute, Micelle, Moderna Therapeutics, Momenta, Monsanto, Muse Biotechnologies, Mylan, Nanobiosym, Nanobiotix, NewBridge Ventures, Noveome Biotherapeutics, Novo Nordisk, Particles for Humanity, Pfizer, Pioneer Hi-Bred International, Polaris Partners, Portal Instruments, Preceres, Pulmatrix, PureTech, ReLive, ReproCELL USA, Rubius Therapeutics, Secant Medical, Seer, Selecta Biosciences, Senses Biosciences, Senses, Setsuro Tech, Seventh Sense Biosystems, Shenzhen Rice Life Technology, Shire AG, Shiseido, Siglion, Sigma-Aldrich, SiO2, SKE S.R.L., Soil Culture Solutions, SQZ Biotechnologies, StemBioSys, Suono Bio, T2 Biosystems, Taconic Biosciences, TARA, Tarveda Therapeutics, Tesio Pharmaceuticals, Third Rock, Tiba Biotech, TISSIUM, TransGen, Translate Bio, TriLink BioTechnologies, Unilever, VasoRx, Verseau Therapeutics, Vivtex, Whitehead Institute, Wiki Foods, YZ Biosciences and Zenomics.
Figures



References
-
- Gates B. Responding to Covid-19 — a once-in-a-century pandemic? N. Engl. J. Med. 2020;382:1677–1679. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. Weekly operational update on COVID-19. 9 September 2020 (WHO, 2020).
-
- Johns Hopkins University. COVID-19 dashboard by the center for systems science and engineering (CSSE) at Johns Hopkins University (JHU). JHUhttps://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html (2020).
-
- Thorp HH. Time to pull together. Science. 2020;367:1282. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
