Scutellarein alleviates the dysfunction of inner blood-retinal-barrier initiated by hyperglycemia-stimulated microglia cells
- PMID: 33078102
- PMCID: PMC7511377
- DOI: 10.18240/ijo.2020.10.05
Scutellarein alleviates the dysfunction of inner blood-retinal-barrier initiated by hyperglycemia-stimulated microglia cells
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the alleviation of scutellarein (SN) against inner blood-retinal-barrier (iBRB) dysfunction in microglia cells stimulated by hyperglycemia and to elucidate the engaged mechanism.
Methods: Microglia BV2 cells were stimulated by using 25 mmol/L D-glucose. The same concentration of mannitol (25 mmol/L) was applied as an isotonic contrast. Real-time PCR, Western-blot assay and immunofluorescence staining assay was performed. The dysfunction of iBRB in vitro was detected by using transendothelial electrical resistance (TEER) assay. Additionally, the leakage of fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-conjugated dextran (70 kDa) was detected.
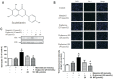
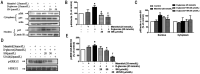
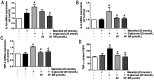
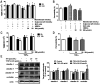
Results: SN abrogated microglia BV2 cells activation and reduced the phosphorylated activation of extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase (ERK)1/2. SN also decreased the transcriptional activation of nuclear factor κB (NFκB) and the elevated expression of tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα), interleukin (IL)-6 and IL-1β in BV2 cells treated with D-glucose (25 mmol/L). SN attenuated iBRB dysfunction in human retinal endothelial cells (HRECs) or choroid-retinal endothelial RF/6A cells when those cells were treated with TNFα, IL-1β or IL-6, or co-cultured with microglia cells stimulated by D-glucose. Moreover, SN restored the decreased protein expression of tight junctions (TJs) in TNFα-treated HRECs and RF/6A cells.
Conclusion: SN not only alleviate iBRB dysfunction via directly inhibiting retinal endothelial injury caused by TNFα, IL-1β or IL-6, but also reduce the release of TNFα, IL-1β and IL-6 from microglia cells by abrogating hyperglycemia-mediated the activation of microglia cells.
Keywords: blood-retinal-barrier; inflammation; scutellarein; tight junctions; tumor necrosis factor α.
International Journal of Ophthalmology Press.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Scutellarin alleviates blood-retina-barrier oxidative stress injury initiated by activated microglia cells during the development of diabetic retinopathy.Biochem Pharmacol. 2019 Jan;159:82-95. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2018.11.011. Epub 2018 Nov 14. Biochem Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30447218
-
Microglia increase tight-junction permeability in coordination with Müller cells under hypoxic condition in an in vitro model of inner blood-retinal barrier.Exp Eye Res. 2021 Apr;205:108490. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2021.108490. Epub 2021 Feb 16. Exp Eye Res. 2021. PMID: 33607076
-
Natural flavonoid galangin alleviates microglia-trigged blood-retinal barrier dysfunction during the development of diabetic retinopathy.J Nutr Biochem. 2019 Mar;65:1-14. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2018.11.006. Epub 2018 Dec 4. J Nutr Biochem. 2019. PMID: 30597356
-
Erythropoietin protects the inner blood-retinal barrier by inhibiting microglia phagocytosis via Src/Akt/cofilin signalling in experimental diabetic retinopathy.Diabetologia. 2021 Jan;64(1):211-225. doi: 10.1007/s00125-020-05299-x. Epub 2020 Oct 26. Diabetologia. 2021. PMID: 33104828
-
Melatonin Maintains Inner Blood-Retinal Barrier by Regulating Microglia via Inhibition of PI3K/Akt/Stat3/NF-κB Signaling Pathways in Experimental Diabetic Retinopathy.Front Immunol. 2022 Mar 15;13:831660. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.831660. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35371022 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Effects of diabetes on microglial physiology: a systematic review of in vitro, preclinical and clinical studies.J Neuroinflammation. 2023 Mar 3;20(1):57. doi: 10.1186/s12974-023-02740-x. J Neuroinflammation. 2023. PMID: 36869375 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in Anti-Diabetic Cognitive Dysfunction Effect of Erigeron Breviscapus (Vaniot) Hand-Mazz.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Dec 29;16(1):50. doi: 10.3390/ph16010050. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36678547 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Metalloproteinases in Diabetes-associated Mild Cognitive Impairment.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2024;23(1):58-74. doi: 10.2174/1570159X22666240517090855. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38963109 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cyclophilin A and C are the Main Components of Extracellular Vesicles in Response to Hyperglycemia in BV2 Microglial Cells.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Aug;62(8):10349-10366. doi: 10.1007/s12035-025-04921-6. Epub 2025 Apr 8. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 40199808 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammatory cytokines as mediators of retinal endothelial barrier dysfunction in non-infectious uveitis.Clin Transl Immunology. 2023 Dec 12;12(12):e1479. doi: 10.1002/cti2.1479. eCollection 2023. Clin Transl Immunology. 2023. PMID: 38090668 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cheung N, Mitchell P, Wong TY. Diabetic retinopathy. Lancet. 2010;376(9735):124–136. - PubMed
-
- Kubo Y, Seko N, Usui T, Akanuma SI, Hosoya KI. Lysosomal trapping is present in retinal capillary endothelial cells: insight into its influence on cationic drug transport at the inner blood-retinal barrier. Biol Pharm Bull. 2016;39(8):1319–1324. - PubMed
-
- Hosoya KI, Tachikawa M. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology. New York, NY: Springer New York; 2013. The inner blood-retinal barrier; pp. 85–104. - PubMed
-
- Campbell M, Humphries P. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology. New York, NY: Springer New York; 2013. The blood-retina barrier; pp. 70–84. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
