Anti-proliferation and apoptosis-inducing effects of sodium aescinate on retinoblastoma Y79 cells
- PMID: 33078103
- PMCID: PMC7511392
- DOI: 10.18240/ijo.2020.10.06
Anti-proliferation and apoptosis-inducing effects of sodium aescinate on retinoblastoma Y79 cells
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the anti-proliferation and apoptosis-inducing effects of sodium aescinate (SA) on retinoblastoma Y79 cells and its mechanism.
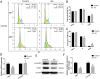
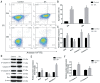
Methods: Y79 cells were cultured at different drug concentrations for different periods of time (24, 48, and 72h). The inhibitory effect of SA on proliferation of Y79 cells was detected by the cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8) assay, and the morphology of Y79 cells in each group was observed under an inverted microscope. An IC50 of 48h was selected for subsequent experiments. After pretreatment with SA for 24 and 48h, cellular DNA distribution and apoptosis were detected by flow cytometry. Real-time qunatitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) and Western blot were used to assess changes in related genes (CDK1, CyclinB1, Bax, Bcl-2, caspase-9, caspase-8, and caspase-3).
Results: SA inhibited proliferation and induced apoptosis of Y79 cells in a time-dependent and concentration-dependent manner. Following its intervention in the cell cycle pathway, SA can inhibit the expression of CDK1 and CyclinB1 at the mRNA and protein levels, and block cells in the G2/M phase. In caspase-related apoptotic pathways, up-regulation of Bax and down-regulation of Bcl-2 caused caspase-9 to self-cleave and further activate caspase-3. What's more, the caspase-8-mediated extrinsic apoptosis pathway was activated, and the activated caspase-8 was released into the cytoplasm to activate caspase-3, which as a member of the downstream apoptotic effect group, initiates a caspase-cascade reaction that induces cell apoptosis.
Conclusion: SA inhibits the proliferation of Y79 cells by arresting the cell cycle at the G2/M phase, and induces apoptosis via the caspase-related apoptosis pathway, indicating that SA may have promising potential as a chemotherapeutic drug.
Keywords: cell cycle arrest; extrinsic apoptosis pathway; intrinsic apoptosis pathway; retinoblastoma; sodium aescinate.
International Journal of Ophthalmology Press.
Figures

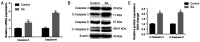
Similar articles
-
Effect of Andrographis paniculata polysaccharide on human retinoblastoma Y79 cell proliferation and apoptosis.Int J Ophthalmol. 2021 Apr 18;14(4):497-503. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2021.04.03. eCollection 2021. Int J Ophthalmol. 2021. PMID: 33875938 Free PMC article.
-
Panax notoginseng saponins induce apoptosis in retinoblastoma Y79 cells via the PI3K/AKT signalling pathway.Exp Eye Res. 2022 Mar;216:108954. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2022.108954. Epub 2022 Jan 21. Exp Eye Res. 2022. PMID: 35074343
-
Long non-coding RNA CCAT1 promotes human retinoblastoma SO-RB50 and Y79 cells through negative regulation of miR-218-5p.Biomed Pharmacother. 2017 Mar;87:683-691. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.01.004. Epub 2017 Jan 12. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017. PMID: 28088735
-
S-Adenosylmethionine Inhibits the Proliferation of Retinoblastoma Cell Y79, Induces Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Arrest of Y79 Cells by Inhibiting the Wnt2/β-Catenin Pathway.Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2024 Oct 4;72(1). doi: 10.2478/aite-2024-0020. eCollection 2024 Jan 1. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2024. PMID: 39362212
-
The apoptotic effects and synergistic interaction of sodium butyrate and MG132 in human retinoblastoma Y79 cells.Cancer Res. 1999 Nov 1;59(21):5586-95. Cancer Res. 1999. PMID: 10554039
Cited by
-
Sodium aescinate promotes apoptosis of pancreatic stellate cells and alleviates pancreatic fibrosis by inhibiting the PI3K/Akt/FOXO1 signaling pathways.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Apr 22;16:1554260. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1554260. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40331192 Free PMC article.
-
A comprehensive retrospect on the current perspectives and future prospects of pneumoconiosis.Front Public Health. 2025 Jan 10;12:1435840. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1435840. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2025. PMID: 39866352 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Solid lipid nanoparticles as an effective sodium aescinate delivery system: formulation and anti-inflammatory activity.RSC Adv. 2022 Feb 24;12(11):6583-6591. doi: 10.1039/d1ra07638h. eCollection 2022 Feb 22. RSC Adv. 2022. PMID: 35424603 Free PMC article.
-
Sodium aescinate-induced hepatotoxicity via ATF4/GSH/GPX4 axis-mediated ferroptosis.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 7;15(1):1141. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-79723-2. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39774712 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yang G, Fu Y, Zhang LX, Lu XY, Li QM. miR106b regulates retinoblastoma Y79 cells through Runx3. Oncol Rep. 2017;38(5):3039–3043. - PubMed
-
- Agnieszka B, Cezary G. Retinoblastoma. Journal of Education, Health and Sport. 2018;8(7):204–213.
-
- Mattosinho CCS, Moura ATMS, Oigman G, Ferman SE, Grigorovski N. Time to diagnosis of retinoblastoma in Latin America: a systematic review. Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2019;36(2):55–72. - PubMed
-
- Dimaras H, Kimani K, Dimba EA, Gronsdahl P, White A, Chan HS, Gallie BL. Retinoblastoma. Lancet. 2012;379(9824):1436–1446. - PubMed
-
- Matsuda H, Li Y, Yoshikawa M. Effects of escins Ia, Ib, IIa, and IIb from horse chestnuts on gastrointestinal transit and ileus in mice. Bioorg Med Chem. 1999;7(8):1737–1741. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
