High mobility group box 3 promotes cervical cancer proliferation by regulating Wnt/β-catenin pathway
- PMID: 33078596
- PMCID: PMC7593223
- DOI: 10.3802/jgo.2020.31.e91
High mobility group box 3 promotes cervical cancer proliferation by regulating Wnt/β-catenin pathway
Abstract
Objective: High mobility group box 3 (HMGB3) plays an important role in the development of various cancer. This study aims to explore whether HMGB3 regulates cervical cancer (CC) progression and elucidate the underlying mechanism.
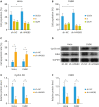
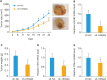
Methods: HMGB3 expression in clinical patients' tumor samples were determined by real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) and western blot. HMGB3 overexpression/knockdown were used to investigate its function. Cell apoptosis and cycle were detected by Annexin V/PI staining and flow cytometry. In vivo tumor model was made by subcutaneous injection of HeLa cells transfected with shRNAs targeting HMGB3 (sh-HMGB31) into the flank area of nude mice. Western blot was used to detect the levels of β-catenin, c-Myc, and matrix metalloproteinase-7 (MMP-7) in Hela and CaSki cells transfected with sh-HMGB3 or shRNAs targeting β-catenin.
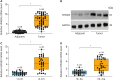
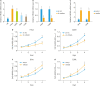
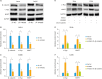
Results: Both messenger RNA and protein levels of HMGB3 were upregulated in CC tissues from patients. High expression level of HMGB3 had positive correlation with serosal invasion, lymph metastasis, and tumor sizes in CC patient. Functional experiments showed that HMGB3 could promote CC cell proliferation both in vitro and in vivo. The expression levels of c-Myc and MMP-7 were increased, resulting in regulating cell apoptosis, cell cycle, and activating Wnt/β-catenin pathway.
Conclusions: Our data indicated that HMGB3 may serve as an oncoprotein. It could be used as a potential prognostic marker and represent a promising therapeutic strategy for CC treatment.
Keywords: Cell Proliferation; Cervical Cancer; HMGB3 Protein; beta Catenin; shRNA.
Copyright © 2020. Asian Society of Gynecologic Oncology, Korean Society of Gynecologic Oncology.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
References
-
- Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 2014;64:9–29. - PubMed
-
- Smith RA, Brooks D, Cokkinides V, Saslow D, Brawley OW. Cancer screening in the United States, 2013: a review of current American Cancer Society guidelines, current issues in cancer screening, and new guidance on cervical cancer screening and lung cancer screening. CA Cancer J Clin. 2013;63:88–105. - PubMed
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90. - PubMed
-
- Smith JS, Green J, Berrington de Gonzalez A, Appleby P, Peto J, Plummer M, et al. Cervical cancer and use of hormonal contraceptives: a systematic review. Lancet. 2003;361:1159–1167. - PubMed
-
- Vaccarella S, Lortet-Tieulent J, Plummer M, Franceschi S, Bray F. Worldwide trends in cervical cancer incidence: impact of screening against changes in disease risk factors. Eur J Cancer. 2013;49:3262–3273. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

