Therapeutic Efficacy of Artemether-Lumefantrine for Uncomplicated Falciparum Malaria in Northern Zambia
- PMID: 33078701
- PMCID: PMC7695049
- DOI: 10.4269/ajtmh.20-0852
Therapeutic Efficacy of Artemether-Lumefantrine for Uncomplicated Falciparum Malaria in Northern Zambia
Abstract
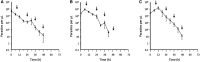
Artemether-lumefantrine (AL) is a first-line agent for uncomplicated malaria caused by Plasmodium falciparum. The WHO recommends periodic therapeutic efficacy studies of antimalarial drugs for the detection of malaria parasite drug resistance and to inform national malaria treatment policies. We conducted a therapeutic efficacy study of AL in a high malaria transmission region of northern Zambia from December 2014 to July 2015. One hundred children of ages 6 to 59 months presenting to a rural health clinic with uncomplicated falciparum malaria were admitted for treatment with AL (standard 6-dose regimen) and followed weekly for 5 weeks. Parasite counts were taken every 6 hours during treatment to assess parasite clearance. Recurrent episodes during follow-up (n = 14) were genotyped to distinguish recrudescence from reinfection and to identify drug resistance single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and multidrug resistance protein 1 (mdr1) copy number variation. Day 7 lumefantrine concentrations were measured for correspondence with posttreatment reinfection. All children who completed the parasite clearance portion of the study (n = 94) were microscopy-negative by 72 hours. The median parasite elimination half-life was 2.7 hours (interquartile range: 2.1-3.3). Genotype-corrected therapeutic efficacy was 98.8% (95% CI: 97.6-100). Purported artemisinin and lumefantrine drug resistance SNPs in atp6, 3D7_1451200, and mdr1 were detected but did not correlate with parasite recurrence, nor did day 7 lumefantrine concentrations. In summary, AL was highly effective for the treatment of uncomplicated falciparum malaria in northern Zambia during the study period. The high incidence of recurrent parasitemia was consistent with reinfection due to high, perennial malaria transmission.
Figures
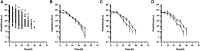

References
-
- World Health Organization , 2009. Methods of Surveillance of Antimalarial Drug Efficacy. Geneva, Switzerland: WHO Global Malaria Programme.
-
- World Health Organization , 2019. World Malaria Report. Geneva, Switzerland: WHO Global Malaria Programme.
-
- Steketee RW, Sipilanyambe N, Chimumbwa J, Banda JJ, Mohamed A, Miller J, Basu S, Miti SK, Campbell CC, 2008. National malaria control and scaling up for impact: the Zambia experience through 2006. Am J Trop Med Hyg 79: 45–52. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

