Multidrug-Resistant Hypervirulent Group B Streptococcus in Neonatal Invasive Infections, France, 2007-2019
- PMID: 33079049
- PMCID: PMC7588536
- DOI: 10.3201/eid2611.201669
Multidrug-Resistant Hypervirulent Group B Streptococcus in Neonatal Invasive Infections, France, 2007-2019
Abstract
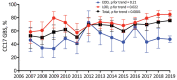
We analyzed group B Streptococcus (GBS) neonatal invasive infections reported during 2007-2019 in France. The hypervirulent clonal complex (CC) 17 GBS was responsible for 66% (827/1,262) of cases. The role of CC17 GBS increased over time (p for trend = 0.0001), together with the emergence of a multidrug-resistant CC17 GBS sublineage.
Keywords: France; GBS; Streptococcus agalactiae; antimicrobial resistance; bacteria; early-onset disease; group B Streptococcus; hypervirulent CC17 clone; late-onset disease; neonatal infections.
Figures

References
-
- Edwards MS, Nizet V, Baker CJ. Group B streptococcal infections. In: Infectious diseases of the fetus and newborn infant. 7th ed. Remington JS, Klein JO, Wilson CB, Nizet V, Maldonado Y, editors. Philadelphia: Elsevier; 2011. p. 419–69.
-
- Bekker V, Bijlsma MW, van de Beek D, Kuijpers TW, van der Ende A. Incidence of invasive group B streptococcal disease and pathogen genotype distribution in newborn babies in the Netherlands over 25 years: a nationwide surveillance study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2014;14:1083–9. 10.1016/S1473-3099(14)70919-3 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Santé Publique France. Bulletin of the bacterial invasive infections surveillance network 2018. [cited 2020 Jan 30]. http://invs.santepubliquefrance.fr/Dossiers-thematiques/Maladies-infecti...
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

