15 Years MR-encephalography
- PMID: 33079327
- PMCID: PMC7910380
- DOI: 10.1007/s10334-020-00891-z
15 Years MR-encephalography
Abstract
Objective: This review article gives an account of the development of the MR-encephalography (MREG) method, which started as a mere 'Gedankenexperiment' in 2005 and gradually developed into a method for ultrafast measurement of physiological activities in the brain. After going through different approaches covering k-space with radial, rosette, and concentric shell trajectories we have settled on a stack-of-spiral trajectory, which allows full brain coverage with (nominal) 3 mm isotropic resolution in 100 ms. The very high acceleration factor is facilitated by the near-isotropic k-space coverage, which allows high acceleration in all three spatial dimensions.
Methods: The methodological section covers the basic sequence design as well as recent advances in image reconstruction including the targeted reconstruction, which allows real-time feedback applications, and-most recently-the time-domain principal component reconstruction (tPCR), which applies a principal component analysis of the acquired time domain data as a sparsifying transformation to improve reconstruction speed as well as quality.
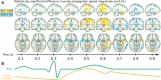
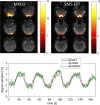
Applications: Although the BOLD-response is rather slow, the high speed acquisition of MREG allows separation of BOLD-effects from cardiac and breathing related pulsatility. The increased sensitivity enables direct detection of the dynamic variability of resting state networks as well as localization of single interictal events in epilepsy patients. A separate and highly intriguing application is aimed at the investigation of the glymphatic system by assessment of the spatiotemporal patterns of cardiac and breathing related pulsatility.
Discussion: MREG has been developed to push the speed limits of fMRI. Compared to multiband-EPI this allows considerably faster acquisition at the cost of reduced image quality and spatial resolution.
Keywords: Functional magnetic resonance imaging; Magnetic resonance imaging.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures














Similar articles
-
The potential of MR-Encephalography for BCI/Neurofeedback applications with high temporal resolution.Neuroimage. 2019 Jul 1;194:228-243. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2019.03.046. Epub 2019 Mar 23. Neuroimage. 2019. PMID: 30910728
-
Three-dimensional MR-encephalography: fast volumetric brain imaging using rosette trajectories.Magn Reson Med. 2011 May;65(5):1260-8. doi: 10.1002/mrm.22711. Epub 2011 Feb 3. Magn Reson Med. 2011. PMID: 21294154
-
Enhanced subject-specific resting-state network detection and extraction with fast fMRI.Hum Brain Mapp. 2017 Feb;38(2):817-830. doi: 10.1002/hbm.23420. Epub 2016 Oct 3. Hum Brain Mapp. 2017. PMID: 27696603 Free PMC article.
-
Improving the sensitivity of spin-echo fMRI at 3T by highly accelerated acquisitions.Magn Reson Med. 2021 Jul;86(1):245-257. doi: 10.1002/mrm.28715. Epub 2021 Feb 23. Magn Reson Med. 2021. PMID: 33624352
-
Functional magnetic resonance imaging.Handb Clin Neurol. 2016;135:61-92. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-444-53485-9.00004-0. Handb Clin Neurol. 2016. PMID: 27432660 Review.
Cited by
-
Increased very low frequency pulsations and decreased cardiorespiratory pulsations suggest altered brain clearance in narcolepsy.Commun Med (Lond). 2022 Sep 30;2:122. doi: 10.1038/s43856-022-00187-4. eCollection 2022. Commun Med (Lond). 2022. PMID: 36193214 Free PMC article.
-
Traumatic brain injury and sleep in military and veteran populations: A literature review.NeuroRehabilitation. 2024;55(3):245-270. doi: 10.3233/NRE-230380. NeuroRehabilitation. 2024. PMID: 39121144 Free PMC article. Review.
-
WHOCARES: WHOle-brain CArdiac signal REgression from highly accelerated simultaneous multi-Slice fMRI acquisitions.J Neural Eng. 2022 Sep 6;19(5):10.1088/1741-2552/ac8bff. doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/ac8bff. J Neural Eng. 2022. PMID: 35998568 Free PMC article.
-
The glymphatic system: Current understanding and modeling.iScience. 2022 Aug 20;25(9):104987. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.104987. eCollection 2022 Sep 16. iScience. 2022. PMID: 36093063 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Delta Wave MRI: fMRI of Electrophysiologic Activity.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2025 Jun 3;46(6):1203-1207. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A8618. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2025. PMID: 39653427
References
-
- Hennig J, Zhong K, Speck O. MR-encephalography: fast multi-channel monitoring of brain physiology with magnetic resonance. Neuroimage. 2007;34:212–219. - PubMed
-
- Littin S, Jia F, Layton KJ, Kroboth S, Yu H, Hennig J, Zaitsev M. Development and implementation of an 84-channel matrix gradient coil. Magn Reson Med. 2018;79:1181–1191. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

