The effect of etidronate on choroidal neovascular activity in patients with pseudoxanthoma elasticum
- PMID: 33079965
- PMCID: PMC7575070
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0240970
The effect of etidronate on choroidal neovascular activity in patients with pseudoxanthoma elasticum
Abstract
Aim: To assess the effect of the bisphosphonate etidronate on choroidal neovascular (CNV) activity in patients with pseudoxanthoma elasticum (PXE).
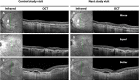
Methods: This is an ancillary study in a single center, randomized, double-blind placebo-controlled trial (RCT) in which 74 patients with PXE were assigned to either one-year etidronate or placebo treatment. Spectral domain optical coherence tomography (SD-OCT) imaging and color fundus photography were performed every three months for one year and were systematically assessed on signs of CNV activity.
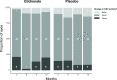
Results: In the etidronate group, 11 (30%) of the patients had CNV activity at baseline, compared to 25 (67%) of the patients in the placebo group (P = 0.005). The proportion of eyes with CNV activity during the study ranged from 18-33% in the etidronate group and 42-56% in the placebo group and no significant difference in improvement or worsening of CNV activity was found (P = 0.168). Using a generalized mixed model for repeated measures, there was a protective effect of etidronate in crude analysis (RR 0.86, 95% CI 0.75-0.98) that disappeared when adjusting for baseline CNV activity (RR 0.97, 95% CI 0.84-1.13).
Conclusion: In this post-hoc RCT analysis we did not observe a protecting or deteriorating effect of etidronate on CNV activity in patients with PXE after adjustment for baseline CNV.
Conflict of interest statement
UNI-Pharma SA provided the etidronate and placebo capsules for free, but was not involved in the design, the execution, the analysis, or the reporting of the Treatment of Ectopic Mineralization in Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum trial. This does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

