Structural Changes in Films of Pulmonary Surfactant Induced by Surfactant Vesicles
- PMID: 33080138
- PMCID: PMC8754419
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.0c01813
Structural Changes in Films of Pulmonary Surfactant Induced by Surfactant Vesicles
Abstract
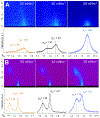
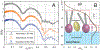
When compressed by the shrinking alveolar surface area during exhalation, films of pulmonary surfactant in situ reduce surface tension to levels at which surfactant monolayers collapse from the surface in vitro. Vesicles of pulmonary surfactant added below these monolayers slow collapse. X-ray scattering here determined the structural changes induced by the added vesicles. Grazing incidence X-ray diffraction on monolayers of extracted calf surfactant detected an ordered phase. Mixtures of dipalmitoyl phosphatidylcholine and cholesterol, but not the phospholipid alone, mimic that structure. At concentrations that stabilize the monolayers, vesicles in the subphase had no effect on the unit cell, and X-ray reflection showed that the film remained monomolecular. The added vesicles, however, produced a concentration-dependent increase in the diffracted intensity. These results suggest that the enhanced resistance to collapse results from enlargement by the additional material of the ordered phase.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

References
-
- Goerke J; Clements JA Alveolar surface tension and lung surfactant. In Handbook of Physiology—The Respiratory System Vol III, Part 1; Macklem PT, Mead J, Ed.; American Physiological Society: Washington, D.C., 1985; Vol. III, pp 247–261.
-
- Bastacky J; Lee CY; Goerke J; Koushafar H; Yager D; Kenaga L; Speed TP; Chen Y; Clements JA Alveolar lining layer is thin and continuous: low-temperature scanning electron microscopy of rat lung. J. Appl. Physiol 1995, 79, 1615–1628. - PubMed
-
- Fisher MJ; Wilson MF; Weber KC Determination of alveolar surface area and tension from in situ pressure-volume data. Respir. Physiol 1970, 10, 159–171. - PubMed
-
- Horie T; Hildebrandt J Dynamic compliance, limit cycles, and static equilibria of excised cat lung. J. Appl. Physiol 1971, 31, 423–430. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

