Resistance-Conferring Mycobacterial Mutations and Quantification of Early Bactericidal Activity
- PMID: 33080154
- PMCID: PMC7924570
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.202007-2740LE
Resistance-Conferring Mycobacterial Mutations and Quantification of Early Bactericidal Activity
Figures
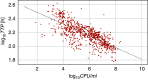
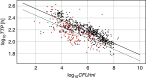
Comment on
-
Early Bactericidal Activity of Different Isoniazid Doses for Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis (INHindsight): A Randomized, Open-Label Clinical Trial.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020 Jun 1;201(11):1416-1424. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201910-1960OC. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020. PMID: 31945300 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dooley KE, Miyahara S, von Groote-Bidlingmaier F, Sun X, Hafner R, Rosenkranz SL, et al. A5312 Study Team. Early bactericidal activity of different isoniazid doses for drug-resistant TB (INHindsight): a randomized open-label clinical trial. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020;201:1416–1424. - PMC - PubMed
-
- O’Sullivan DM, McHugh TD, Gillespie SH. Mapping the fitness of Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains: a complex picture. J Med Microbiol. 2010;59:1533–1535. - PubMed
-
- Friedrich SO, Rachow A, Saathoff E, Singh K, Mangu CD, Dawson R, et al. Pan African Consortium for the Evaluation of Anti-tuberculosis Antibiotics (PanACEA) Assessment of the sensitivity and specificity of Xpert MTB/RIF assay as an early sputum biomarker of response to tuberculosis treatment. Lancet Respir Med. 2013;1:462–470. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

