Functional Diversification of SRSF Protein Kinase to Control Ubiquitin-Dependent Neurodevelopmental Signaling
- PMID: 33080171
- PMCID: PMC7725506
- DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2020.09.025
Functional Diversification of SRSF Protein Kinase to Control Ubiquitin-Dependent Neurodevelopmental Signaling
Abstract
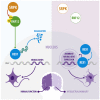
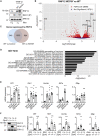
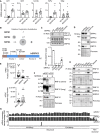
Conserved protein kinases with core cellular functions have been frequently redeployed during metazoan evolution to regulate specialized developmental processes. The Ser/Arg (SR)-rich splicing factor (SRSF) protein kinase (SRPK), which is implicated in splicing regulation, is one such conserved eukaryotic kinase. Surprisingly, we show that SRPK has acquired the capacity to control a neurodevelopmental ubiquitin signaling pathway. In mammalian embryonic stem cells and cultured neurons, SRPK phosphorylates Ser-Arg motifs in RNF12/RLIM, a key developmental E3 ubiquitin ligase that is mutated in an intellectual disability syndrome. Processive phosphorylation by SRPK stimulates RNF12-dependent ubiquitylation of nuclear transcription factor substrates, thereby acting to restrain a neural gene expression program that is aberrantly expressed in intellectual disability. SRPK family genes are also mutated in intellectual disability disorders, and patient-derived SRPK point mutations impair RNF12 phosphorylation. Our data reveal unappreciated functional diversification of SRPK to regulate ubiquitin signaling that ensures correct regulation of neurodevelopmental gene expression.
Keywords: development; metazoan evolution; neural development; neurodevelopmental disorders; protein kinase; protein phosphorylation; signal transduction; stem cells; transcriptomics; ubiquitin signaling.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Ackerman S.L., Kozak L.P., Przyborski S.A., Rund L.A., Boyer B.B., Knowles B.B. The mouse rostral cerebellar malformation gene encodes an UNC-5-like protein. Nature. 1997;386:838–842. - PubMed
-
- Batson J., Toop H.D., Redondo C., Babaei-Jadidi R., Chaikuad A., Wearmouth S.F., Gibbons B., Allen C., Tallant C., Zhang J. Development of potent, selective SRPK1 inhibitors as potential topical therapeutics for neovascular eye disease. ACS Chem. Biol. 2017;12:825–832. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

