SARS-CoV-2 Disrupts Splicing, Translation, and Protein Trafficking to Suppress Host Defenses
- PMID: 33080218
- PMCID: PMC7543886
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.10.004
SARS-CoV-2 Disrupts Splicing, Translation, and Protein Trafficking to Suppress Host Defenses
Abstract
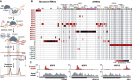
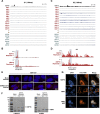
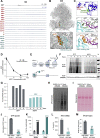
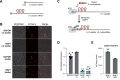
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is a recently identified coronavirus that causes the respiratory disease known as coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Despite the urgent need, we still do not fully understand the molecular basis of SARS-CoV-2 pathogenesis. Here, we comprehensively define the interactions between SARS-CoV-2 proteins and human RNAs. NSP16 binds to the mRNA recognition domains of the U1 and U2 splicing RNAs and acts to suppress global mRNA splicing upon SARS-CoV-2 infection. NSP1 binds to 18S ribosomal RNA in the mRNA entry channel of the ribosome and leads to global inhibition of mRNA translation upon infection. Finally, NSP8 and NSP9 bind to the 7SL RNA in the signal recognition particle and interfere with protein trafficking to the cell membrane upon infection. Disruption of each of these essential cellular functions acts to suppress the interferon response to viral infection. Our results uncover a multipronged strategy utilized by SARS-CoV-2 to antagonize essential cellular processes to suppress host defenses.
Keywords: NSP1; NSP16; NSP8; NSP9; RNA-protein interactions; SARS-CoV-2; interferon; mRNA splicing; protein trafficking; translation.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures








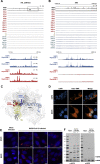

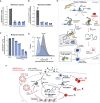
References
-
- Alexopoulou L., Holt A.C., Medzhitov R., Flavell R.A. Recognition of double-stranded RNA and activation of NF-kappaB by Toll-like receptor 3. Nature. 2001;413:732–738. - PubMed
-
- Ameismeier M., Cheng J., Berninghausen O., Beckmann R. Visualizing late states of human 40S ribosomal subunit maturation. Nature. 2018;558:249–253. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- F30 CA247447/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007616/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL130007/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM008042/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 GM115516/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P20 GM125498/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- F30 HL136080/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 HL120877/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA040612/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 GM118228/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R41 AI132047/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- U01 AI141997/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

