Designed variants of ACE2-Fc that decouple anti-SARS-CoV-2 activities from unwanted cardiovascular effects
- PMID: 33080267
- PMCID: PMC7568492
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.10.120
Designed variants of ACE2-Fc that decouple anti-SARS-CoV-2 activities from unwanted cardiovascular effects
Abstract
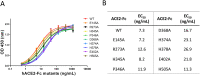
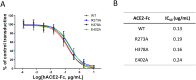
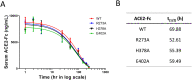
Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) is the entry receptor for SARS-CoV-2, and recombinant ACE2 decoys are being evaluated as new antiviral therapies. We designed and tested an antibody-like ACE2-Fc fusion protein, which has the benefit of long pharmacological half-life and the potential to facilitate immune clearance of the virus. Out of a concern that the intrinsic catalytic activity of ACE2 may unintentionally alter the balance of its hormonal substrates and cause adverse cardiovascular effects in treatment, we performed a mutagenesis screening for inactivating the enzyme. Three mutants, R273A, H378A and E402A, completely lost their enzymatic activity for either surrogate or physiological substrates. All of them remained capable of binding SARS-CoV-2 and could suppress the transduction of a pseudotyped virus in cell culture. This study established new ACE2-Fc candidates as antiviral treatment for SARS-CoV-2 without potentially harmful side effects from ACE2's catalytic actions toward its vasoactive substrates.
Keywords: ACE2-Fc; COVID-19; Mutagenesis; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest Jing Jin and Pan Liu have applied for a provisional patent of the ACE2-Fc mutants described in the article.
Figures
References
-
- Zhou P., Yang X.L., Wang X.G., Hu B., Zhang L., Zhang W., Si H.R., Zhu Y., Li B., Huang C.L., Chen H.D., Chen J., Luo Y., Guo H., Jiang R.D., Liu M.Q., Chen Y., Shen X.R., Wang X., Zheng X.S., Zhao K., Chen Q.J., Deng F., Liu L.L., Yan B., Zhan F.X., Wang Y.Y., Xiao G.F., Shi Z.L. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature. 2020;579(7798):270–273. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hoffmann M., Kleine-Weber H., Schroeder S., Kruger N., Herrler T., Erichsen S., Schiergens T.S., Herrler G., Wu N.H., Nitsche A., Muller M.A., Drosten C., Pohlmann S. SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor. Cell. 2020;181(2):271–280. (e8) - PMC - PubMed
-
- Vickers C., Hales P., Kaushik V., Dick L., Gavin J., Tang J., Godbout K., Parsons T., Baronas E., Hsieh F., Acton S., Patane M., Nichols A., Tummino P. 277(17) 2002. Hydrolysis of Biological Peptides by Human Angiotensin-converting Enzyme-related Carboxypeptidase; pp. 14838–14843. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

