Isatuximab as monotherapy and combined with dexamethasone in patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma
- PMID: 33080623
- PMCID: PMC7933767
- DOI: 10.1182/blood.2020008209
Isatuximab as monotherapy and combined with dexamethasone in patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma
Abstract
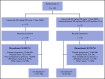
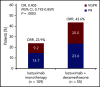
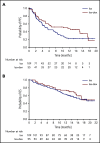
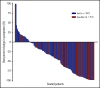
This phase 2 study evaluated isatuximab as monotherapy or combined with dexamethasone in relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma (RRMM). Patients had RRMM refractory to an immunomodulatory drug (IMiD) and a proteasome inhibitor (PI) or had received ≥3 prior lines of therapy incorporating an IMiD and PI. Patients received isatuximab either as monotherapy (20 mg/kg on days 1, 8, 15, and 22 [once weekly] of cycle 1 followed by 20 mg/kg on days 1 and 15 of subsequent cycles; Isa group) or in combination with dexamethasone (40 mg/d [20 mg/d in patients aged ≥75 years] once weekly; Isa-dex group). Treated patients (N = 164) had received a median of 4 (range, 2-10) prior treatment lines. Patients received a median of 5 (1-24) and 7 (1-22) treatment cycles; at data cutoff, 13 (11.9%) of 109 and 15 (27.3%) of 55 patients remained on treatment in the Isa and Isa-dex arms, respectively. Overall response rate (primary efficacy end point) was 23.9% in the Isa arm and 43.6% in the Isa-dex arm (odds ratio, 0.405; 95% confidence interval, 0.192-0.859; P = .008). Median progression-free survival and overall survival were 4.9 and 18.9 months for Isa, and 10.2 and 17.3 months for Isa-dex. Infusion reactions (mostly grade 1/2) and hematologic abnormalities were the most common adverse events. There was a similar incidence of grade 3 or higher infections in both groups (22.0% and 21.8%). In conclusion, addition of dexamethasone to isatuximab increased response rates and survival outcomes with no detrimental effect on safety. This trial was registered at www.clinicaltrials.gov as #NCT01084252.
© 2021 by The American Society of Hematology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: M.D. has received honoraria from Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, Janssen, and Takeda. S.B. reports consultancy for Janssen-Cilag and Takeda; has received honoraria from Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, and Janssen; and an advisory role with Amgen, Celgene, Janssen, and Karyopharm. P.A. reports consultancy for Takeda and an advisory role with Amgen, Janssen, and Takeda. M. Capra reports speakers bureau for Amgen, Janssen, and Roche. M. Cavo reports consultancy, honoraria, and speakers bureau for Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, Janssen, and Takeda; and other from Janssen and Celgene. C.C. has received travel/accommodation expenses from Amgen. C.G. reports consultancy for Celgene, Millennium, and Onyx; has received honoraria from Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, and Millennium; reports speakers bureau and travel/accommodation expenses from Celgene and Millennium; and research funding from Celgene. V.H. reports consultancy/advisory board for AbbVie, Amgen, Celgene, Janssen, Sanofi, and Takeda; and speakers bureau for Amgen, Celgene, Janssen, Sanofi, and Takeda. M.J. reports consultancy/honoraria/speakers bureau for AbbVie, Celgene, Janssen, Novartis, and Takeda. V.V. reports consultancy for Biocad, Janssen, and Roche; and speakers bureau for Astellas, Bristol Myers Squibb, Janssen, Roche, and Takeda. J.Y.Y., R.S., and S.M. are employees of Sanofi. M.H. is an employee of Ividata, working for Sanofi. B.P. has received honoraria for lectures from and membership on advisory boards with Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, Janssen, Merck, Novartis, Roche, and Sanofi; unrestricted grants from Celgene, EngMab, Sanofi, and Takeda; and consultancy for Celgene, Janssen, Sanofi, and Takeda. R.V. has received honoraria and travel expenses from Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, Janssen, Merck, Novartis, Onyx, and Takeda; and research funding from Onyx and Takeda. E.Y.R. declares no competing financial interests.
Figures


Comment in
-
Dexamethasone as a partner of isatuximab.Blood. 2021 Mar 4;137(9):1133-1134. doi: 10.1182/blood.2020009268. Blood. 2021. PMID: 33661291 No abstract available.
References
-
- Lin P, Owens R, Tricot G, Wilson CS. Flow cytometric immunophenotypic analysis of 306 cases of multiple myeloma. Am J Clin Pathol. 2004;121(4):482-488. - PubMed
-
- US Food and Drug Administration . Highlights of prescribing information: Sarclisa (isatuximab-irfc); 2020. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/761113s000lbl.pdf. Accessed 26 August 2020.
-
- European Medicines Agency . Sarclisa, summary of product characteristics; 2020. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/sarclisa-epar.... Accessed 29 October 2020.
-
- Moreno L, Perez C, Zabaleta A, et al. . The mechanism of action of the anti-CD38 monoclonal antibody isatuximab in multiple myeloma. Clin Cancer Res. 2019;25(10):3176-3187. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

