Modestly Elevated Serum Procalcitonin Levels in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Free of Active Infection
- PMID: 33080909
- PMCID: PMC7603207
- DOI: 10.3390/medicina56100545
Modestly Elevated Serum Procalcitonin Levels in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Free of Active Infection
Abstract
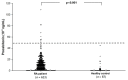
Background and objectives: To investigate the serum procalcitonin (PCT) levels among patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) without active infection compared with healthy controls and to understand the relationship of PCT with RA disease activity, and treatment received by patients. Materials and Methods: Patients aged 20 years and above with clinician-confirmed diagnosis of RA and healthy volunteers were included during regular outpatient visits, and those with active infection symptoms and signs were excluded. RA disease activity was measured using the Disease Activity Score-28 for Rheumatoid Arthritis with erythrocyte sedimentation rate (DAS28-ESR). Medications received by the patients were also recorded. Results: A total of 623 patients with RA and 87 healthy subjects were recruited in this study. The mean PCT were significantly higher in patients with RA (6.90 ± 11.81 × 10-3 ng/mL) compared with healthy controls (1.70 ± 6.12 × 10-3 ng/mL) (p < 0.001) and the difference remained statistically significant after adjusting for age and sex. In addition, multiple linear regression analysis showed that a lower rank-transformed PCT serum level was significantly correlated with the use of biologics (p = 0.017) and a high DAS28-ESR score (p = 0.028) in patients with RA. Conclusion: Patients with RA have a significantly higher serum PCT levels compared with healthy controls. The use of biologics and an active RA disease activity were associated with a lower level of PCT in patients with RA. Further investigation is required to determine the optimal cutoff value of PCT among patients with RA and its association with disease activity and biologic usage.
Keywords: disease activity; disease activity index; infection; procalcitonin; rheumatoid arthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Diagnostic Value of Interleukin 6, Interleukin 12P70, Serum Amyloid A, and Procalcitonin for Rheumatoid Arthritis and Their Relationship With the Disease Activity].Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024 Jul 20;55(4):995-1000. doi: 10.12182/20240760107. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024. PMID: 39170004 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Procalcitonin is a specific marker for detecting bacterial infection in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.J Rheumatol. 2012 Aug;39(8):1517-23. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.111601. Epub 2012 Jul 1. J Rheumatol. 2012. PMID: 22753652
-
High Level Serum Procalcitonin Associated Gouty Arthritis Susceptibility: From a Southern Chinese Han Population.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 16;10(7):e0132855. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0132855. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26182343 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Sanhuangyilong decoction plus methotrexate on tumor necrosis factor alpha and interferon gamma in serum and synovial fluid in rheumatoid arthritis patients with symptom pattern of damp heat obstruction.J Tradit Chin Med. 2016 Oct;36(5):625-33. doi: 10.1016/s0254-6272(16)30082-6. J Tradit Chin Med. 2016. PMID: 29933531 Clinical Trial.
-
Infliximab equivalently suppresses oxidative stress compared to tocilizumab among well-controlled patients with rheumatoid arthritis.Int J Rheum Dis. 2018 Oct;21(10):1815-1821. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.12972. Epub 2016 Oct 24. Int J Rheum Dis. 2018. PMID: 27778459
Cited by
-
Future Biomarkers for Infection and Inflammation in Rheumatoid Arthritis.J Inflamm Res. 2023 Jun 29;16:2719-2726. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S413579. eCollection 2023. J Inflamm Res. 2023. PMID: 37404716 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Elevated Serum Presepsin Identifies Herpes Simplex Virus-1 Reactivation in COVID-19 Patients.Viruses. 2025 Feb 28;17(3):357. doi: 10.3390/v17030357. Viruses. 2025. PMID: 40143286 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shi Y., Peng J.M., Hu X.Y., Wang Y. The utility of initial procalcitonin and procalcitonin clearance for prediction of bacterial infection and outcome in critically ill patients with autoimmune diseases: A prospective observational study. BMC Anesthesiol. 2015;15:137. doi: 10.1186/s12871-015-0122-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

