Simultaneous Qualitative and Quantitative Evaluation of the Coptidis Rhizoma and Euodiae Fructus Herbal Pair by Using UHPLC-ESI-QTOF-MS and UHPLC-DAD
- PMID: 33081031
- PMCID: PMC7587604
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25204782
Simultaneous Qualitative and Quantitative Evaluation of the Coptidis Rhizoma and Euodiae Fructus Herbal Pair by Using UHPLC-ESI-QTOF-MS and UHPLC-DAD
Abstract
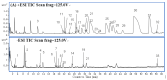
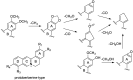
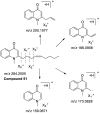
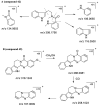
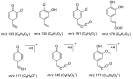
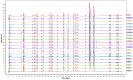
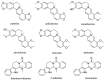
The herbal pair of Coptidis Rhizoma (CR) and Euodiae Fructus (EF) is a classical traditional Chinese medicine formula used for treating gastro-intestinal disorders. In this study, we established a systematic method for chemical profiling and quantification analysis of the major constituents in the CR-EF herbal pair. A method of ultra high performance liquid chromatography/quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UHPLC-QTOF-MS) for qualitative analysis was developed. Sixty-five compounds, including alkaloids, phenolics, and limonoids, were identified or tentatively assigned by comparison with reference standards or literature data. The UHPLC fingerprints of 19 batches of the CR-EF herbal pair samples were obtained and the reference fingerprint chromatograms were established. Furthermore, nine compounds among 24 common peaks of fingerprints were considered as marker components, which either had high contents or significant bioactivities, were applied to quality control of the CR-EF herbal pair by quantitative analysis. This UHPLC-DAD analysis method was validated by precision, linearity, repeatability, stability, recovery, and so on. The method was simple and sensitive, and thus reliable for quantitative and chemical fingerprint analysis for the quality evaluation and control of the CR-EF herbal pair and related traditional Chinese medicines.
Keywords: Coptidis Rhizoma; Euodiae Fructus; UHPLC-DAD fingerprint; UHPLC-ESI-QTOF-MS; herbal pair; quality markers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

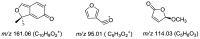
References
-
- Xiang J.L., Lui Y., Bai Q.Y., Xu Y. Research advances in pharmacological action and clinical application of Zuojin Pill. Inform. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2004;21:5–7.
-
- Wang Q.S., Cui Y.L., Dong T.J., Zhang X.F., Lin K.M. Ethanol extract from a Chinese herbal formula, “Zuojin Pill”, inhibit the expression of inflammatory mediators in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 mouse macrophages. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012;141:377–385. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2012.02.049. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zhang H.M., Wang C.H., Wang Z.T. Simultaneous analysis of protoberberine and indolequinoline alkaloids in Zuojin Pill extract by high-performance liquid chromatography. Acta Chromatogr. 2013;25:589–600. doi: 10.1556/AChrom.25.2013.3.14. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

