First Case of KRT2 Epidermolytic Nevus and Novel Clinical and Genetic Findings in 26 Italian Patients with Keratinopathic Ichthyoses
- PMID: 33081034
- PMCID: PMC7593923
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21207707
First Case of KRT2 Epidermolytic Nevus and Novel Clinical and Genetic Findings in 26 Italian Patients with Keratinopathic Ichthyoses
Abstract
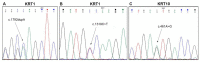
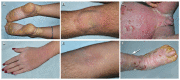
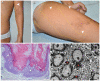
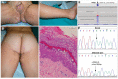
Keratinopathic ichthyoses (KI) are a clinically heterogeneous group of keratinization disorders due to mutations in KRT1, KTR10, or KRT2 genes encoding keratins of suprabasal epidermis. Characteristic clinical features include superficial blisters and erosions in infancy and progressive development of hyperkeratosis. Histopathology shows epidermolytic hyperkeratosis. We describe the clinical, histopathological, and molecular findings of a series of 26 Italian patients from 19 unrelated families affected with (i) epidermolytic ichthyosis due to KRT1 or KRT10 mutations (7 and 9 cases, respectively); (ii) KTR10-mutated ichthyosis with confetti (2 cases); (iii) KRT2-mutated superficial epidermolytic ichthyosis (5 cases); and (iv) KRT10-mutated epidermolytic nevus (2 cases). Of note, molecular genetic testing in a third case of extensive epidermolytic nevus revealed a somatic missense mutation (p.Asn186Asp) in the KRT2 gene, detected in DNA from lesional skin at an allelic frequency of 25% and, at very low frequency (1.5%), also in blood. Finally, we report three novel dominant mutations, including a frameshift mutation altering the C-terminal V2 domain of keratin 1 in three familiar cases presenting a mild phenotype. Overall, our findings expand the phenotypic and molecular spectrum of KI and show for the first time that epidermolytic nevus can be due to somatic KRT2 mutation.
Keywords: KRT1; KRT10; KRT2; epidermal nevus; epidermolytic ichthyosis; histopathology; ichthyosis with confetti; keratin; superficial epidermolytic ichthyosis; ultrastructure.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Deep Phenotyping of Superficial Epidermolytic Ichthyosis due to a Recurrent Mutation in KRT2.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 14;23(14):7791. doi: 10.3390/ijms23147791. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35887135 Free PMC article.
-
Expanding the Clinical and Genetic Spectrum of KRT1, KRT2 and KRT10 Mutations in Keratinopathic Ichthyosis.Acta Derm Venereol. 2016 May;96(4):473-8. doi: 10.2340/00015555-2299. Acta Derm Venereol. 2016. PMID: 26581228
-
Epidermolytic epidermal nevus caused by a somatic mutation in KRT2.Pediatr Dermatol. 2021 Mar;38(2):538-540. doi: 10.1111/pde.14529. Epub 2021 Feb 8. Pediatr Dermatol. 2021. PMID: 33555633
-
[Clinical presentation and etiology of ichthyoses. Overview of the new nomenclature and classification].Hautarzt. 2010 Oct;61(10):891-902; quiz 903-4. doi: 10.1007/s00105-010-2018-4. Hautarzt. 2010. PMID: 20827455 Review. German.
-
Annular Epidermolytic Ichthyosis Mimicking Greither Disease: A Case Report and Literature Review.Am J Case Rep. 2022 Feb 24;23:e935393. doi: 10.12659/AJCR.935393. Am J Case Rep. 2022. PMID: 35202349 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Epidermolytic ichthyosis: Clinical spectrum and burden of disease in a large German cohort.J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2025 May;39(5):1028-1037. doi: 10.1111/jdv.20096. Epub 2024 May 13. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2025. PMID: 38741524 Free PMC article.
-
Deep Phenotyping of Superficial Epidermolytic Ichthyosis due to a Recurrent Mutation in KRT2.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 14;23(14):7791. doi: 10.3390/ijms23147791. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35887135 Free PMC article.
-
Post Zygotic, Somatic, Deletion in KERATIN 1 V1 Domain Generates Structural Alteration of the K1/K10 Dimer, Producing a Monolateral Palmar Epidermolytic Nevus.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 27;22(13):6901. doi: 10.3390/ijms22136901. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34199056 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and genetic findings in 13 Chinese children with keratinopathic ichthyosis.Pediatr Investig. 2023 Jul 15;7(3):168-176. doi: 10.1002/ped4.12391. eCollection 2023 Sep. Pediatr Investig. 2023. PMID: 37736367 Free PMC article.
-
Somatic Variants of KRT1/KRT10 Identified by Next-generation Sequencing in Patients with Epidermal Nevi.Acta Derm Venereol. 2024 Oct 22;104:adv40958. doi: 10.2340/actadv.v104.40958. Acta Derm Venereol. 2024. PMID: 39439178 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Oji V., Tadini G., Akiyama M., Bardon C.B., Bodemer C., Bourrat E., Coudiere P., DiGiovanna J.J., Elias P., Fischer J., et al. Revised nomenclature and classification of inherited ichthyoses: Results of the First Ichthyosis Consensus Conference in Sorèze 2009. J. Am. Acad. Derm. 2010;63:607–641. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2009.11.020. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

