A Facile Approach for Rapid Prototyping of Microneedle Molds, Microwells and Micro-Through-Holes in Various Substrate Materials Using CO2 Laser Drilling
- PMID: 33081055
- PMCID: PMC7603185
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines8100427
A Facile Approach for Rapid Prototyping of Microneedle Molds, Microwells and Micro-Through-Holes in Various Substrate Materials Using CO2 Laser Drilling
Abstract
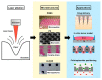
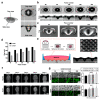
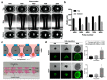
CO2 laser manufacturing has served as an enabling and reliable tool for rapid and cost-effective microfabrication over the past few decades. While a wide range of industrial and biological applications have been studied, the choice of materials fabricated across various laser parameters and systems is often confounded by their complex combinations. We herein presented a unified procedure performed using percussion CO2 laser drilling with a range of laser parameters, substrate materials and various generated microstructures, enabling a variety of downstream tissue/cellular-based applications. Emphasis is placed on delineating the laser drilling effect on different biocompatible materials and proof-of-concept utilities. First, a polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) microneedle (MN) array mold is fabricated to generate dissolvable polyvinylpyrrolidone/polyvinyl alcohol (PVP/PVA) MNs for transdermal drug delivery. Second, polystyrene (PS) microwells are optimized in a compact array for the formation of size-controlled multicellular tumor spheroids (MCTSs). Third, coverglass is perforated to form a microaperture that can be used to trap/position cells/spheroids. Fourth, the creation of through-holes in PS is validated as an accessible method to create channels that facilitate medium exchange in hanging drop arrays and as a conducive tool for the growth and drug screenings of MCTSs.
Keywords: CO2 laser; hanging drops; microneedle; microwells; multicellular tumor spheroids; rapid prototyping.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Wu W.I., Rezai P., Hsu H.H., Selvaganapathy P.R. Materials and methods for the microfabrication of microfluidic biomedical devices. In: Li X.J., Zhou Y., editors. Microfluidic Devices for Biomedical Applications. Woodhead Publishing; Cambridge, UK: 2013. pp. 3–62.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

