Regulation of Reactive Oxygen Species-Mediated Damage in the Pathogenesis of Schizophrenia
- PMID: 33081261
- PMCID: PMC7603028
- DOI: 10.3390/brainsci10100742
Regulation of Reactive Oxygen Species-Mediated Damage in the Pathogenesis of Schizophrenia
Abstract
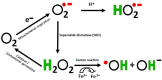
The biochemical integrity of the brain is paramount to the function of the central nervous system, and oxidative stress is a key contributor to cerebral biochemical impairment. Oxidative stress, which occurs when an imbalance arises between the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and the efficacy of the antioxidant defense mechanism, is believed to play a role in the pathophysiology of various brain disorders. One such disorder, schizophrenia, not only causes lifelong disability but also induces severe emotional distress; however, because of its onset in early adolescence or adulthood and its progressive development, consuming natural antioxidant products may help regulate the pathogenesis of schizophrenia. Therefore, elucidating the functions of ROS and dietary antioxidants in the pathogenesis of schizophrenia could help formulate improved therapeutic strategies for its prevention and treatment. This review focuses specifically on the roles of ROS and oxidative damage in the pathophysiology of schizophrenia, as well as the effects of nutrition, antipsychotic use, cognitive therapies, and quality of life on patients with schizophrenia. By improving our understanding of the effects of various nutrients on schizophrenia, it may become possible to develop nutritional strategies and supplements to treat the disorder, alleviate its symptoms, and facilitate long-term recovery.
Keywords: Schizophrenia; antioxidants; antipsychotics; nutrients; oxidative stress; reactive oxygen species.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Oxidative stress involvement in schizophrenia pathophysiology: a review].Encephale. 2006 Mar-Apr;32(2 Pt 1):244-52. doi: 10.1016/s0013-7006(06)76151-6. Encephale. 2006. PMID: 16910626 Review. French.
-
Oxidative stress and role of antioxidant and omega-3 essential fatty acid supplementation in schizophrenia.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2001 Apr;25(3):463-93. doi: 10.1016/s0278-5846(00)00181-0. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2001. PMID: 11370992 Review.
-
Prevention of oxidative stress-mediated neuropathology and improved clinical outcome by adjunctive use of a combination of antioxidants and omega-3 fatty acids in schizophrenia.Int Rev Psychiatry. 2006 Apr;18(2):119-31. doi: 10.1080/09540260600581993. Int Rev Psychiatry. 2006. PMID: 16777666 Review.
-
Free radicals, antioxidant defense systems, and schizophrenia.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2013 Oct 1;46:200-6. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2013.02.015. Epub 2013 Mar 5. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2013. PMID: 23470289 Review.
-
Roles of antioxidant enzymes in corpus luteum rescue from reactive oxygen species-induced oxidative stress.Reprod Biomed Online. 2012 Dec;25(6):551-60. doi: 10.1016/j.rbmo.2012.08.004. Epub 2012 Sep 12. Reprod Biomed Online. 2012. PMID: 23063822 Review.
Cited by
-
Most Effective Combination of Nutraceuticals for Improved Memory and Cognitive Performance in the House Cricket, Acheta domesticus.Nutrients. 2021 Jan 25;13(2):362. doi: 10.3390/nu13020362. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 33504066 Free PMC article.
-
Serum NOX1 and Raftlin as New Potential Biomarkers of Interest in Schizophrenia: A Preliminary Study.Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2022 Nov 2;18:2519-2527. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S385631. eCollection 2022. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2022. PMID: 36349345 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of Guanine-Based Purines on the Oxidoreductive Reactions Involved in Normal or Altered Brain Functions.J Clin Med. 2023 Feb 1;12(3):1172. doi: 10.3390/jcm12031172. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 36769818 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nutrition, nutritional deficiencies, and schizophrenia: An association worthy of constant reassessment.World J Clin Cases. 2021 Oct 6;9(28):8295-8311. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i28.8295. World J Clin Cases. 2021. PMID: 34754840 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Audiovisual Interactions on Working Memory Task Performance-Interference or Facilitation.Brain Sci. 2022 Jul 6;12(7):886. doi: 10.3390/brainsci12070886. Brain Sci. 2022. PMID: 35884692 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nagano T., Mizuno M., Morita K., Nawa H. Pathological implications of oxidative stress in patients and animal models with schizophrenia: The role of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling. Curr. Top. Behav. Neurosci. 2016;29:429–446. - PubMed
-
- Gonzalez-Liencres C., Tas C., Brown E.C., Erdin S., Onur E., Cubukcoglu Z., Aydemir O., Aysen Esen-Danaci A., Brüne M. Oxidative stress in schizophrenia: A case–control study on the effects on social cognition and neurocognition. BMC Psychiatry. 2014;14:268. doi: 10.1186/s12888-014-0268-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

