Roles of ABCC1 and ABCC4 in Proliferation and Migration of Breast Cancer Cell Lines
- PMID: 33081264
- PMCID: PMC7589126
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21207664
Roles of ABCC1 and ABCC4 in Proliferation and Migration of Breast Cancer Cell Lines
Abstract
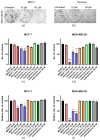
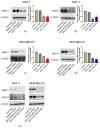
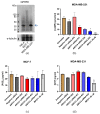
ABCC1 and ABCC4 utilize energy from ATP hydrolysis to transport many different molecules, including drugs, out of the cell and, as such, have been implicated in causing drug resistance. However recently, because of their ability to transport signaling molecules and inflammatory mediators, it has been proposed that ABCC1 and ABCC4 may play a role in the hallmarks of cancer development and progression, independent of their drug efflux capabilities. Breast cancer is the most common cancer affecting women. In this study, the aim was to investigate whether ABCC1 or ABCC4 play a role in the proliferation or migration of breast cancer cell lines MCF-7 (luminal-type, receptor-positive) and MDA-MB-231 (basal-type, triple-negative). The effects of small molecule inhibitors or siRNA-mediated knockdown of ABCC1 or ABCCC4 were measured. Colony formation assays were used to assess the clonogenic capacity, MTT assays to measure the proliferation, and scratch assays and Transwell assays to monitor the cellular migration. The results showed a role for ABCC1 in cellular proliferation, whilst ABCC4 appeared to be more important for cellular migration. ELISA studies implicated cAMP and/or sphingosine-1-phosphate efflux in the mechanism by which these transporters mediate their effects. However, this needs to be investigated further, as it is key to understand the mechanisms before they can be considered as targets for treatment.
Keywords: MRP1; MRP4; breast cancer; cAMP; invasion; migration; proliferation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
ABCC1-Exported Sphingosine-1-phosphate, Produced by Sphingosine Kinase 1, Shortens Survival of Mice and Patients with Breast Cancer.Mol Cancer Res. 2018 Jun;16(6):1059-1070. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-17-0353. Epub 2018 Mar 9. Mol Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 29523764 Free PMC article.
-
ABC transporters and neuroblastoma.Adv Cancer Res. 2015;125:139-70. doi: 10.1016/bs.acr.2014.10.005. Epub 2015 Jan 8. Adv Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 25640269
-
Tryptophan hydroxylase 1 and 5-HT7 receptor preferentially expressed in triple-negative breast cancer promote cancer progression through autocrine serotonin signaling.Mol Cancer. 2016 Nov 21;15(1):75. doi: 10.1186/s12943-016-0559-6. Mol Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27871326 Free PMC article.
-
Substrates and inhibitors of human multidrug resistance associated proteins and the implications in drug development.Curr Med Chem. 2008;15(20):1981-2039. doi: 10.2174/092986708785132870. Curr Med Chem. 2008. PMID: 18691054 Review.
-
The A-B-C of small-molecule ABC transport protein modulators: From inhibition to activation-a case study of multidrug resistance-associated protein 1 (ABCC1).Med Res Rev. 2019 Nov;39(6):2031-2081. doi: 10.1002/med.21573. Epub 2019 Apr 3. Med Res Rev. 2019. PMID: 30941807 Review.
Cited by
-
Restoring microRNA-34a overcomes acquired drug resistance and disease progression in human breast cancer cell lines via suppressing the ABCC1 gene.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2024 Feb;204(1):133-149. doi: 10.1007/s10549-023-07170-0. Epub 2023 Dec 7. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2024. PMID: 38057687 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Ferroptosis-Mediated Modification Patterns and Tumor Immune Microenvironment Characterization in Uveal Melanoma.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jul 27;9:685120. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.685120. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34386492 Free PMC article.
-
Leisure Activities, Genetic Risk, and Frailty: Evidence from the Chinese Adults Aged 80 Years or Older.Gerontology. 2023;69(8):961-971. doi: 10.1159/000530665. Epub 2023 Apr 19. Gerontology. 2023. PMID: 37075711 Free PMC article.
-
SiRNF8 Delivered by DNA Framework Nucleic Acid Effectively Sensitizes Chemotherapy in Colon Cancer.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 Jan 6;19:171-188. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S437859. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 38204601 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of ABC Transporters in Lipid Metabolism and the Comorbid Course of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease and Atherosclerosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 23;22(13):6711. doi: 10.3390/ijms22136711. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34201488 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

