Snacks and The City: Unexpected Low Sales of an Easy-Access, Tasty, and Healthy Snack at an Urban Snacking Hotspot
- PMID: 33081280
- PMCID: PMC7589805
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph17207538
Snacks and The City: Unexpected Low Sales of an Easy-Access, Tasty, and Healthy Snack at an Urban Snacking Hotspot
Abstract
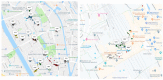
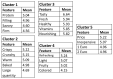
: While many people declare an intention to eat and snack more healthily, a large body of research has found that these intentions often do not translate into actual behavior. This failure to fulfil intentions is regularly attributed to the obesogenic environment, on which basis it is assumed that changing the food environment may lead to more healthy snacking behavior. To test this premise in real life practice, the present research project investigated whether making a healthy snack easy-to-access in an urban environment characterized by unhealthy snacking would support people in their intentions of purchasing more healthy snacks. The urban snack project consisted of three phases. In Phase 1, a hotspot location for unhealthy snacking was determined by using a Global Positioning System to track people's snacking locations anda survey to verify the location . In Phase 2, an attractive snack was developed that met consumers' criteria of what constituted a healthy and tasty snack, together with corresponding branding that also included a small food truck from which to sell the newly developed snacks. In Phase 3, the snack was sold from the food truck located at the previously determined unhealthy snacking hotspot. We counted the number of snacks sold and canvassed people's opinions about the snack and its branding, finding that in spite of people's appreciation for the snack, the food truck, and the branding, actual sales of the snack were very low. In the Discussion, we name predominant eating and purchasing habits as possible reasons for these low sales. Future research could focus on placing the healthy snack directly beside people's habitual snack purchase location to ensure that the new choice gets better recognized. Overall, the findings suggest that merely placing healthy snacks more prominently in people's food environment is not sufficient to lead people to snack more healthily.
Keywords: food marketing; nudging intervention; nutrition education; public health; urban field experiment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Cleveland L.E., Goldman J.D., Moshfegh A.M. Contribution of snacks to food and nutrient intakes in the United States. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. J. 2005;19:A88.
-
- Forslund H.B., Torgerson J.S., Sjöström L., Lindroos A.K. Snacking frequency in relation to energy intake and food choices in obese men and women compared to a reference population. Int. J. Obes. 2005;29:711–719. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

