Evaluation of Changes in the Levels of Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes Phyla of Sheep Feces Depending on the Breed
- PMID: 33081312
- PMCID: PMC7603071
- DOI: 10.3390/ani10101901
Evaluation of Changes in the Levels of Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes Phyla of Sheep Feces Depending on the Breed
Abstract
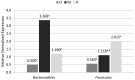
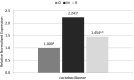
Studies carried out so far have indicated the effect of the microbiome on the composition of ruminant products. Recent studies have shown that not only diet, but also genetic factors can affect the microbiological composition of the digestive system. The aim of the study was to determine the differences in the levels of selected bacterial phyla in terms of breed differences. Three sheep breeds, i.e., Olkuska, Romanov, and old-type Polish Merino, differing in their use (meat-wool, meat, prolificacy) and country of breed origin were included in the study. Sheep at the same age and of the same sex were kept for a period of 3 months in the same environmental conditions and fed the same feed in the same proportions. The study included real-time PCR (polymerase chain reaction) analysis of feces collected before the slaughter and measurements of body weight and chilled carcasses. The obtained results showed significant differences between the breeds in the levels of bacterial populations tested. There were also differences in body weight between the breeds during the first weight measurements, however, the final results did not show any differences-after three months of maintenance all of them reached similar body weights, despite differences in fecal microbiological composition. The study suggests that in addition to diet and environmental conditions, the microbiology can also be influenced by breed.
Keywords: breed; microbiome; ruminants; sheep.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Selected bacteria in sheep stool depending on breed and physiology state.Sci Rep. 2023 Jul 20;13(1):11739. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-38785-4. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37474553 Free PMC article.
-
Inter and intraspecies comparison of the level of selected bacterial phyla in in cattle and sheep based on feces.BMC Vet Res. 2021 Jun 25;17(1):224. doi: 10.1186/s12917-021-02922-w. BMC Vet Res. 2021. PMID: 34172061 Free PMC article.
-
The Level of Selected Bacterial Phyla on the Skin Surface of Small Ruminants According to the Breed and Species.Animals (Basel). 2021 Sep 18;11(9):2734. doi: 10.3390/ani11092734. Animals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34573700 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Breed on the Fecal Microbiome of Dogs under the Same Dietary Condition.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019 Dec 28;29(12):1947-1956. doi: 10.4014/jmb.1906.06048. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 31601060
-
Hair sheep genetic resources and their contribution to diversified small ruminant production in the United States.J Anim Sci. 1997 Mar;75(3):630-40. doi: 10.2527/1997.753630x. J Anim Sci. 1997. PMID: 9078477 Review.
Cited by
-
Selected bacteria in sheep stool depending on breed and physiology state.Sci Rep. 2023 Jul 20;13(1):11739. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-38785-4. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37474553 Free PMC article.
-
Inter and intraspecies comparison of the level of selected bacterial phyla in in cattle and sheep based on feces.BMC Vet Res. 2021 Jun 25;17(1):224. doi: 10.1186/s12917-021-02922-w. BMC Vet Res. 2021. PMID: 34172061 Free PMC article.
-
Glutathione S-transferase (GST) and cortisol levels vs. microbiology of the digestive system of sheep during lambing.BMC Vet Res. 2022 Mar 18;18(1):107. doi: 10.1186/s12917-022-03201-y. BMC Vet Res. 2022. PMID: 35303874 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between rumen microbial differences and traits among Hu sheep, Tan sheep, and Dorper sheep.J Anim Sci. 2022 Sep 1;100(9):skac261. doi: 10.1093/jas/skac261. J Anim Sci. 2022. PMID: 35953151 Free PMC article.
-
Fecal shedding level of Haemonchus contortus is associated with gastrointestinal bacterial microbial composition in naturally infected sheep.Rev Bras Parasitol Vet. 2025 Feb 3;34(1):e017724. doi: 10.1590/S1984-29612025005. eCollection 2025. Rev Bras Parasitol Vet. 2025. PMID: 39907368 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

