Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in relation to the risk of all-cause mortality and cardiovascular events in patients with chronic kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 33081569
- PMCID: PMC7668415
- DOI: 10.1080/0886022X.2020.1832521
Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in relation to the risk of all-cause mortality and cardiovascular events in patients with chronic kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Aim: To systematically evaluate the relationship between the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and the risk of all-cause mortality or cardiovascular events in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD).
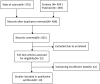
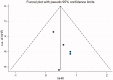
Methods: PubMed, Embase, and Web of Science databases were searched for cohort studies that were published since the databases were launched, until 1 April 2020. We selected papers according to specific inclusion and exclusion criteria, extracted data, and evaluated the quality of the citations. Data from eligible studies were used to calculate the combined hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% confidence intervals (CI).
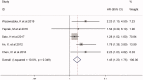
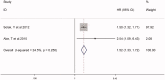
Results: The search identified 1048 potentially eligible records, and 10 studies (n = 1442) were selected. Eight studies reported all-cause mortality, and two studies reported cardiovascular events. The combined HR of all-cause mortality was 1.45 (95% CI 1.20-1.75) and the HR of cardiovascular events was 1.52 (95% CI 1.33-1.72) when NLR was considered as a categorical variable. Similarly, the association between NLR and all-cause mortality was confirmed (HR 1.35; 95% CI 1.23-1.48) when NLR was used as a continuous variable.
Conclusion: NLR is a predictor of all-cause mortality and cardiovascular events in patients with chronic kidney disease.
Keywords: All-cause mortality; cardiovascular events; meta-analysis; neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures

References
-
- Peng F, Li Z, Yi C, et al. . Platelet index levels and cardiovascular mortality in incident peritoneal dialysis patients: a cohort study. Platelets. 2017;28(6):576–584. - PubMed
-
- Valga F, Monzon T, Henriquez F, et al. . Prognostic role of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio for mortality in incident hemodialysis patients. 3 years follow-up study. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2019;34(Suppl_1):a303.
-
- Diaz-Martinez J, Campa A, Delgado-Enciso I, et al. . The relationship of blood neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio with nutrition markers and health outcomes in hemodialysis patients. Int Urol Nephrol. 2019;51(7):1239–1247. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
