PGE2 upregulates gene expression of dual oxidase in a lepidopteran insect midgut via cAMP signalling pathway
- PMID: 33081632
- PMCID: PMC7653354
- DOI: 10.1098/rsob.200197
PGE2 upregulates gene expression of dual oxidase in a lepidopteran insect midgut via cAMP signalling pathway
Abstract
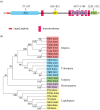
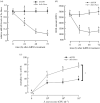
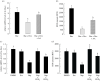
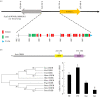
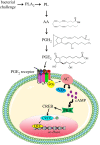
In insect midgut, prostaglandins (PGs) play a crucial role in defending bacterial and malarial pathogens. However, little is known about the PG signalling pathway in the midgut. A dual oxidase (Se-Duox) with presumed function of catalysing reactive oxygen species (ROS) production in the midgut was identified in beet armyworm, Spodoptera exigua. Se-Duox was expressed in all developmental stages, exhibiting relatively high expression levels in the midgut of late larval instars. Se-Duox expression was upregulated upon bacterial challenge. RNA interference (RNAi) of Se-Duox expression significantly suppressed ROS levels in the midgut lumen. The suppression of ROS levels increased insecticidal activity of Serratia marcescens after oral infection. Interestingly, treatment with a PLA2 inhibitor prevented the induction of Se-Duox expression in response to bacterial challenge. On the other hand, addition of its catalytic product rescued the induction of Se-Duox expression. Especially, PG synthesis inhibitor significantly suppressed Se-Duox expression, while the addition of PGE2 or PGD2 rescued the inhibition. Subsequent PG signals involved cAMP and downstream components because specific inhibitors of cAMP signal components such as adenylate cyclase (AC) and protein kinase A (PKA) significantly inhibited Se-Duox expression. Indeed, addition of a cAMP analogue stimulated Se-Duox expression in the midgut. Furthermore, individual RNAi specific to PGE2 receptor (a trimeric G-protein subunit), AC, PKA or cAMP-responsive element-binding protein resulted in suppression of Se-Duox expression. These results suggest that PGs can activate midgut immunity via cAMP signalling pathway by inducing Se-Duox expression along with increased ROS levels.
Keywords: Spodoptera exigua; cAMP; dual oxidase; gut immunity; prostaglandin; reactive oxygen species.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare we have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Midgut microorganisms transformed into hemolymph pathogens: Mediating DUOX-ROS immune response to regulate the insecticidal activity of Bacillus thuringiensis against Spodoptera exigua.Pestic Biochem Physiol. 2025 Sep;213:106477. doi: 10.1016/j.pestbp.2025.106477. Epub 2025 May 25. Pestic Biochem Physiol. 2025. PMID: 40744602
-
The role of 20-hydroxyecdysone and juvenile hormone in insecticidal activity of Bacillus thuringiensis regulated by DUOX-ROS immunity in Spodoptera exigua.Pestic Biochem Physiol. 2025 Mar;208:106222. doi: 10.1016/j.pestbp.2024.106222. Epub 2024 Nov 29. Pestic Biochem Physiol. 2025. PMID: 40015833
-
Dorsal switch protein 1 as a damage signal in insect gut immunity to activate dual oxidase via an eicosanoid, PGE2.Front Immunol. 2022 Nov 10;13:994626. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.994626. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36439105 Free PMC article.
-
Paradoxical roles of dual oxidases in cancer biology.Free Radic Biol Med. 2017 Sep;110:117-132. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2017.05.024. Epub 2017 May 31. Free Radic Biol Med. 2017. PMID: 28578013 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antimicrobial actions of dual oxidases and lactoperoxidase.J Microbiol. 2018 Jun;56(6):373-386. doi: 10.1007/s12275-018-7545-1. Epub 2018 Jun 1. J Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29858825 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Repat33 Acts as a Downstream Component of Eicosanoid Signaling Pathway Mediating Immune Responses of Spodoptera exigua, a Lepidopteran Insect.Insects. 2021 May 14;12(5):449. doi: 10.3390/insects12050449. Insects. 2021. PMID: 34069069 Free PMC article.
-
HMGB1-Like Dorsal Switch Protein 1 Triggers a Damage Signal in Mosquito Gut to Activate Dual Oxidase via Eicosanoids.J Innate Immun. 2022;14(6):657-672. doi: 10.1159/000524561. Epub 2022 May 5. J Innate Immun. 2022. PMID: 35512659 Free PMC article.
-
High-throughput screening of caterpillars as a platform to study host-microbe interactions and enteric immunity.Nat Commun. 2022 Nov 24;13(1):7216. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-34865-7. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 36433960 Free PMC article.
-
A soil fungus confers plant resistance against a phytophagous insect by disrupting the symbiotic role of its gut microbiota.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Mar 7;120(10):e2216922120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2216922120. Epub 2023 Feb 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 36848561 Free PMC article.
-
Eicosanoid Signaling in Insect Immunology: New Genes and Unresolved Issues.Genes (Basel). 2021 Feb 1;12(2):211. doi: 10.3390/genes12020211. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33535438 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

