Costs and healthcare utilisation of patients with heart failure in Spain
- PMID: 33081776
- PMCID: PMC7576860
- DOI: 10.1186/s12913-020-05828-9
Costs and healthcare utilisation of patients with heart failure in Spain
Abstract
Background: Increasing the knowledge about heart failure (HF) costs and their determinants is important to ascertain how HF management can be optimized, leading to a significant decrease of HF costs. This study evaluated the cumulative costs and healthcare utilisation in HF patients in Spain.
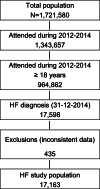
Methods: Observational, retrospective, population-based study using BIG-PAC database, which included data from specialized and primary care of people ≥18 years, from seven autonomous communities in Spain, who received care for HF between 2015 and 2019. The healthcare and medication costs were summarized on a yearly basis starting from the index date (1st January 2015), and then cumulatively until 2019.
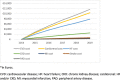
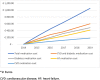
Results: We identified 17,163 patients with HF (year 2015: mean age 77.3 ± 11.8 years, 53.5% men, 51.7% systolic HF, 43.6% on NYHA functional class II). During the 2015-2019 period, total HF associated costs reached 15,373 Euros per person, being cardiovascular disease hospitalizations the most important determinant (75.8%), particularly HF hospitalizations (51.0%). Total medication cost accounted for 7.0% of the total cost. During this period, there was a progressive decrease of cardiovascular disease hospital costs per year (from 2834 Euros in 2015 to 2146 Euros in 2019, P < 0.001), as well as cardiovascular and diabetic medication costs.
Conclusions: During the 2015-2019 period, costs of HF patients in Spain were substantial, being HF hospitalizations the most important determinant. Medication costs represented only a small proportion of total costs. Improving HF management, particularly through the use of drugs that reduce HF hospitalization may be helpful to reduce HF burden.
Keywords: DAPA-HF; Dapagliflozin; Heart failure; Heart failure cost; Hospitalization; Sacubitril/valsartan.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Costs and healthcare utilisation of patients with chronic kidney disease in Spain.BMC Health Serv Res. 2021 Jun 1;21(1):536. doi: 10.1186/s12913-021-06566-2. BMC Health Serv Res. 2021. PMID: 34074269 Free PMC article.
-
Healthcare resource utilization and costs among patients with heart failure with preserved, mildly reduced, and reduced ejection fraction in Spain.BMC Health Serv Res. 2022 Oct 8;22(1):1241. doi: 10.1186/s12913-022-08614-x. BMC Health Serv Res. 2022. PMID: 36209120 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical characteristics, management, and one-year risk of complications among patients with heart failure with and without type 2 diabetes in Spain.Rev Clin Esp (Barc). 2022 Apr;222(4):195-204. doi: 10.1016/j.rceng.2021.04.005. Epub 2021 Sep 10. Rev Clin Esp (Barc). 2022. PMID: 34511336
-
Burden of hospitalization for heart failure in the United States: a systematic literature review.J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2022 Feb;28(2):157-167. doi: 10.18553/jmcp.2022.28.2.157. J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2022. PMID: 35098748 Free PMC article.
-
Sacubitril/Valsartan in Real-Life Practice: Experience in Patients with Advanced Heart Failure and Systematic Review.Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2019 Jun;33(3):307-314. doi: 10.1007/s10557-019-06858-0. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2019. PMID: 30820802
Cited by
-
Gender differences in clinical features and outcomes of patients over 75 years presenting with acute heart failure. Results of a nationwide study (2016-2019).Cardiol J. 2024;31(3):427-433. doi: 10.5603/cj.95612. Epub 2024 Jan 22. Cardiol J. 2024. PMID: 38247437 Free PMC article.
-
Outcomes and factors associated with mortality in patients with atrial fibrillation and heart failure: FARAONIC study.Clin Cardiol. 2023 Nov;46(11):1390-1397. doi: 10.1002/clc.24106. Epub 2023 Aug 18. Clin Cardiol. 2023. PMID: 37596723 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing the impact of haemodynamic monitoring with CardioMEMS on heart failure patients: a cost-benefit analysis.ESC Heart Fail. 2024 Aug;11(4):1955-1962. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.14698. Epub 2024 Mar 18. ESC Heart Fail. 2024. PMID: 38500304 Free PMC article.
-
[Diagnosis and treatment of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction].Herz. 2025 Aug;50(4):297-304. doi: 10.1007/s00059-025-05324-y. Epub 2025 Jul 2. Herz. 2025. PMID: 40601041 German.
-
Design and Development of a Heterogeneous Active Assisted Living Solution for Monitoring and Following Up with Chronic Heart Failure Patients in Spain.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Nov 19;22(22):8961. doi: 10.3390/s22228961. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36433557 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yancy CW, Jessup M, Bozkurt B, et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/HFSA focused update of the 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the Management of Heart Failure: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association task force on clinical practice guidelines and the Heart Failure Society of America. Circulation. 2017;136:e137–e161. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000509. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

