Prevalence of Panton-Valentine leukocidin in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus clinical isolates at a university hospital in Northern Cyprus: a pilot study
- PMID: 33081819
- PMCID: PMC7576721
- DOI: 10.1186/s13104-020-05339-0
Prevalence of Panton-Valentine leukocidin in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus clinical isolates at a university hospital in Northern Cyprus: a pilot study
Abstract
Objective: Panton-Valentine leukocidin (PVL)-positive methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is a healthcare problem worldwide. There are no reports on the virulence characteristics of MRSA in Northern Cyprus (NC). This study aimed to determine the presence of pvl among MRSA isolates from patients admitted to a university hospital in NC using molecular methods. Fifty S. aureus strains were included in this study. BD Phoenix automated identification system was used for bacterial identification and antibiotic susceptibility testing. Methicillin resistance was confirmed by disc diffusion assay. Presence of nuc and mecA genes was tested by multiplex PCR. Detection of pvl gene was performed by single-target PCR.
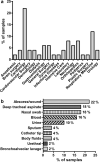
Results: Out of 50 S. aureus isolates identified as MRSA by BD Phoenix system, 3 were susceptible to cefoxitin with disc diffusion assay and were confirmed as methicillin-sensitive S. aureus (MSSA). All isolates (n = 50, 100%) tested positive for the presence nuc gene and 68% (n = 34/50) were mecA positive. pvl was detected in 27.7% (n = 13/47) of the MRSA isolates. Among PVL-positive MRSA isolates, 69.2% (9/13) were inpatients. PVL-MRSA was more common in isolates from deep tracheal aspirate (30.8%, 4/13) and abscess/wound (23.1%, 3/13). This represents the first study of PVL presence among MRSA in hospital setting in NC.
Keywords: Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus; Northern Cyprus; PCR; Panton-Valentine leukocidin; Prevalence; Virulence.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Investigation of the presence of mecC and Panton-Valentine leukocidin genes in Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from clinical specimens during seven years period].Mikrobiyol Bul. 2015 Oct;49(4):594-9. doi: 10.5578/mb.9871. Mikrobiyol Bul. 2015. PMID: 26649417 Turkish.
-
[Investigation of SCCmec types and Panton-Valentine leukocidin in community-acquired and nosocomial Staphylococcus aureus strains: comparing skin and soft tissue infections to the other infections].Mikrobiyol Bul. 2012 Jul;46(3):341-51. Mikrobiyol Bul. 2012. PMID: 22951646 Turkish.
-
Characterisation of clinical Staphylococcus aureus isolates harbouring mecA or Panton-Valentine leukocidin genes from four tertiary care hospitals in Indonesia.Trop Med Int Health. 2016 May;21(5):610-8. doi: 10.1111/tmi.12692. Epub 2016 Mar 30. Trop Med Int Health. 2016. PMID: 26970318
-
Epidemiology of clinically isolated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and its susceptibility to linezolid and vancomycin in Egypt: a systematic review with meta-analysis.BMC Infect Dis. 2023 Apr 26;23(1):263. doi: 10.1186/s12879-023-08202-2. BMC Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 37101125 Free PMC article.
-
Whole-genome sequencing links cases dispersed in time, place, and person while supporting healthcare worker management in an outbreak of Panton-Valentine leucocidin meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus; and a review of literature.J Hosp Infect. 2023 Nov;141:88-98. doi: 10.1016/j.jhin.2023.08.019. Epub 2023 Sep 9. J Hosp Infect. 2023. PMID: 37678435 Review.
Cited by
-
Antimicrobial resistance and virulence profiling of Staphylococcus pseudintermedius isolated from cats, Bangladesh.Vet Q. 2024 Dec;44(1):1-11. doi: 10.1080/01652176.2024.2326848. Epub 2024 Mar 15. Vet Q. 2024. PMID: 38487883 Free PMC article.
-
Biofilm formation, methicillin resistance and SCCmec types among Staphylococcus aureus isolated from clinical samples from a tertiary care hospital, in Nepal.BMC Infect Dis. 2025 Apr 15;25(1):534. doi: 10.1186/s12879-025-10943-1. BMC Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 40234825 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular detection of mecA and lukSF-PV in patients with Staphylococcus aureus soft tissue infections in a tertiary hospital setting, Calabar, Nigeria: a cross-sectional study.Ther Adv Infect Dis. 2025 Jul 20;12:20499361251357394. doi: 10.1177/20499361251357394. eCollection 2025 Jan-Dec. Ther Adv Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 40692858 Free PMC article.
-
Screening of Toxin Genes in Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Clinical Isolates from a Hospital Setting in a Tertiary Hospital in Northern Cyprus.Pol J Microbiol. 2022 Nov 12;71(4):491-497. doi: 10.33073/pjm-2022-042. eCollection 2022 Dec 1. Pol J Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36368015 Free PMC article.
-
Carriage and antimicrobial susceptibility patterns of rectal ESBL E. coli in surgical patients at the University Teaching Hospitals in Lusaka, Zambia.JAC Antimicrob Resist. 2024 Oct 9;6(5):dlae159. doi: 10.1093/jacamr/dlae159. eCollection 2024 Oct. JAC Antimicrob Resist. 2024. PMID: 39386376 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stefani S, Goglio A. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: related infections and antibiotic resistance. Int J Infect Dis. 2010;14:S19–S22. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

