Expamers: a new technology to control T cell activation
- PMID: 33082362
- PMCID: PMC7575567
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-74595-8
Expamers: a new technology to control T cell activation
Abstract
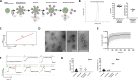
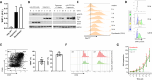
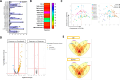
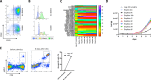
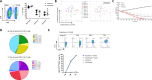
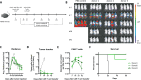
T cell activation is a cornerstone in manufacturing of T cell-based therapies, and precise control over T cell activation is important in the development of the next generation T-cell based therapeutics. This need cannot be fulfilled by currently available methods for T cell stimulation, in particular not in a time dependent manner. Here, we describe a modular activation reagent called Expamers, which addresses these limitations. Expamers are versatile stimuli that are intended for research and clinical use. They are readily soluble and can be rapidly bound and removed from the cell surface, allowing nearly instantaneous initiation and termination of activation signal, respectively. Hence, Expamers enable precise regulation of T cell stimulation duration and provide promise of control over T cell profiles in future products. Expamers can be easily adopted to different T cell production formats and have the potential to increase efficacy of T cell immunotherapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
M.P.P., P.G., C.T., M.W., V.C., B.B., S.D., T.S., D.H.B., M.E., S.P.F., C.S., and L.G. are currently employed by Juno Therapeutics GmbH A Bristol-Myers Squibb Company and own stock of Bristol-Myers Squibb. D.K. and S.R. are currently employed by Juno Therapeutics Inc. A Bristol-Myers Squibb Company and own stock of Bristol-Myers Squibb. L.G., T.S., P.G., M.P.P., and C.S. are listed as inventors on previously filed related patent applications.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Novel DNA-based T-Cell Activator Promotes Rapid T-Cell Activation and Expansion.J Immunother. 2020 Oct;43(8):231-235. doi: 10.1097/CJI.0000000000000329. J Immunother. 2020. PMID: 32796275 Free PMC article.
-
Magnetic field-induced T cell receptor clustering by nanoparticles enhances T cell activation and stimulates antitumor activity.ACS Nano. 2014 Mar 25;8(3):2252-60. doi: 10.1021/nn405520d. Epub 2014 Feb 24. ACS Nano. 2014. PMID: 24564881 Free PMC article.
-
Bifunctional iRGD-anti-CD3 enhances antitumor potency of T cells by facilitating tumor infiltration and T-cell activation.J Immunother Cancer. 2021 May;9(5):e001925. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2020-001925. J Immunother Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33986122 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of various culture conditions on ex vivo expansion of polyclonal T cells for adoptive immunotherapy.APMIS. 2019 Dec;127(12):737-745. doi: 10.1111/apm.12981. Epub 2019 Oct 21. APMIS. 2019. PMID: 31273832 Review.
-
Artificial Methods for T Cell Activation: Critical Tools in T Cell Biology and T Cell Immunotherapy.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1064:207-219. doi: 10.1007/978-981-13-0445-3_13. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018. PMID: 30471035 Review.
Cited by
-
Activation-inducible CAR expression enables precise control over engineered CAR T cell function.Commun Biol. 2023 Jun 5;6(1):604. doi: 10.1038/s42003-023-04978-w. Commun Biol. 2023. PMID: 37277433 Free PMC article.
-
Current and future concepts for the generation and application of genetically engineered CAR-T and TCR-T cells.Front Immunol. 2023 Mar 6;14:1121030. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1121030. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36949949 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PET-based tracking of CAR T cells and viral gene transfer using a cell surface reporter that binds to lanthanide complexes.Nat Biomed Eng. 2025 Jun 13. doi: 10.1038/s41551-025-01415-7. Online ahead of print. Nat Biomed Eng. 2025. PMID: 40514433
-
Attenuating CD3 affinity in a PSMAxCD3 bispecific antibody enables killing of prostate tumor cells with reduced cytokine release.J Immunother Cancer. 2021 Jun;9(6):e002488. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2021-002488. J Immunother Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34088740 Free PMC article.
-
Optimizing CAR-T treatment: A T2EVOLVE guide to raw and starting material selection.Mol Ther. 2025 Mar 5;33(3):847-865. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2024.11.017. Epub 2024 Nov 12. Mol Ther. 2025. PMID: 39533710 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Huppa JB, Davis MM. T-cell-antigen recognition and the immunological synapse. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2003;3:973–983. - PubMed
-
- Garlie NK, LeFever AV, Siebenlist RE, Levine BL, June CH, Lum LG. T cells coactivated with immobilized anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 as potential immunotherapy for cancer. J. Immunother. 1999;22:336. - PubMed
-
- Trickett A, Kwan YL. T cell stimulation and expansion using anti-CD3/CD28 beads. J. Immunol. Methods. 2003;275:251. - PubMed
-
- Riddell SR, Greenberg PD. The use of anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 monoclonal antibodies to clone and expand human antigen-specific T cells. J. Immunol. Methods. 1990;128:189–201. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

