Novel and potent antimicrobial effects of caspofungin on drug-resistant Candida and bacteria
- PMID: 33082485
- PMCID: PMC7576149
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-74749-8
Novel and potent antimicrobial effects of caspofungin on drug-resistant Candida and bacteria
Abstract
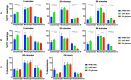
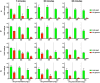
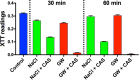
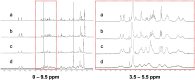
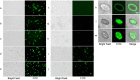
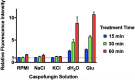
Echinocandins, including caspofungin, micafungin, and anidulafungin, are first-line antifungal agents for the treatment of invasive candidiasis. They exhibit fungicidal activity by inhibiting the synthesis of β-1,3-D-glucan, an essential component of the fungal cell wall. However, they are active only against proliferating fungal cells and unable to completely eradicate fungal cells even after a 24 h drug exposure in standard time-kill assays. Surprisingly, we found that caspofungin, when dissolved in low ionic solutions, had rapid and potent antimicrobial activities against multidrug-resistant (MDR) Candida and bacteria cells even in non-growth conditions. This effect was not observed in 0.9% NaCl or other ion-containing solutions and was not exerted by other echinocandins. Furthermore, caspofungin dissolved in low ionic solutions drastically reduced mature biofilm cells of MDR Candida auris in only 5 min, as well as Candida-bacterial polymicrobial biofilms in a catheter-lock therapy model. Caspofungin displayed ion concentration-dependent conformational changes and intracellular accumulation with increased reactive oxygen species production, indicating a novel mechanism of action in low ionic conditions. Importantly, caspofungin dissolved in 5% glucose water did not exhibit increased toxicity to human cells. This study facilitates the development of new therapeutic strategies in the management of catheter-related biofilm infections.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Brown, G. D. et al. Hidden killers: human fungal infections. Sci. Transl. Med.4, 165rv113 (2012). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

