The Effectiveness of Perampanel for Myoclonic Seizures in Down Syndrome with Isodicentric Chromosome 21
- PMID: 33082764
- PMCID: PMC7548920
- DOI: 10.1159/000508357
The Effectiveness of Perampanel for Myoclonic Seizures in Down Syndrome with Isodicentric Chromosome 21
Abstract
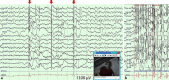
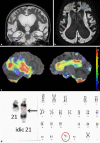
Epileptic seizures are common in the elderly Down syndrome population. We encountered a patient with Down syndrome in whom karyotyping showed the rare isodicentric chromosome 21 and who suffered from myoclonic seizures. A 52-year-old woman with Down syndrome experienced sudden onset of drowsiness and frequent myoclonic jerks in the upper body. Video-EEG recordings demonstrated generalized polyspike-wave discharges consistent with myoclonic jerks, which were exacerbated by photo-stimulation. Her myoclonus completely resolved with perampanel administration. Perampanel was effective for myoclonic seizures in our patient. We suggest that perampanel is an option as first-line therapy for epilepsy and myoclonus in elderly Down syndrome patients.
Keywords: Down syndrome; Epilepsy; Isodicentric chromosome 21; Myoclonus; Perampanel.
Copyright © 2020 by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Late-onset myoclonic epilepsy in Down's syndrome (LOMEDS).Seizure. 2002 Apr;11 Suppl A:303-5. Seizure. 2002. PMID: 12185765
-
Late-onset myoclonic epilepsy in Down's syndrome (LOMEDS).Seizure. 2001 Jun;10(4):303-6. doi: 10.1053/seiz.2000.0500. Seizure. 2001. PMID: 11466028
-
Epilepsy with myoclonic-atonic seizures (Doose syndrome): When video-EEG polygraphy holds the key to syndrome diagnosis.Epilepsy Behav Case Rep. 2015 Oct 28;5:31-3. doi: 10.1016/j.ebcr.2015.10.001. eCollection 2016. Epilepsy Behav Case Rep. 2015. PMID: 26958468 Free PMC article.
-
Myoclonic-astatic epilepsy of early childhood--clinical and EEG analysis of myoclonic-astatic seizures, and discussions on the nosology of the syndrome.Brain Dev. 2001 Nov;23(7):757-64. doi: 10.1016/s0387-7604(01)00281-9. Brain Dev. 2001. PMID: 11701290 Review.
-
Treatment of typical absence seizures and related epileptic syndromes.Paediatr Drugs. 2001;3(5):379-403. doi: 10.2165/00128072-200103050-00006. Paediatr Drugs. 2001. PMID: 11393330 Review.
References
-
- De Simone R, Puig XS, Gélisse P, Crespel A, Genton P. Senile myoclonic epilepsy: delineation of a common condition associated with Alzheimer's disease in Down syndrome. Seizure. 2010 Sep;19((7)):383–9. - PubMed
-
- d'Orsi G, Specchio LM, Apulian Study Group on Senile Myoclonic Epilepsy Progressive myoclonus epilepsy in Down syndrome patients with dementia. J Neurol. 2014 Aug;261((8)):1584–97. - PubMed
-
- Putra M, Surti U, Hu J, Steele D, Clemens M, Saller DN, et al. Beyond Down syndrome phenotype: paternally derived isodicentric chromosome 21 with partial monosomy 21q22.3. Am J Med Genet A. 2017 Dec;173((12)):3153–7. - PubMed
-
- Flores-Ramírez F, Palacios-Guerrero C, García-Delgado C, Morales-Jiménez AB, Arias-Villegas CM, Cervantes A, et al. Cytogenetic profile in 1,921 cases of trisomy 21 syndrome. Arch Med Res. 2015 Aug;46((6)):484–9. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

