Analysis of the IGS rRNA Region and Applicability for Leishmania (V.) braziliensis Characterization
- PMID: 33083046
- PMCID: PMC7559751
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/8885070
Analysis of the IGS rRNA Region and Applicability for Leishmania (V.) braziliensis Characterization
Abstract
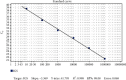
The causative species is an important factor influencing the evolution of American cutaneous leishmaniasis (ACL). Due to its wide distribution in endemic areas, Leishmania (V.) braziliensis is considered one of the most important species in circulation in Brazil. Molecular targets derived from ribosomal RNA (rRNA) were used in studies to identify Leishmania spp.; however, the Intergenic Spacer (IGS) region has not yet been explored in parasite species differentiation. Besides, there is a shortage of sequences deposited in public repositories for this region. Thus, it was proposed to analyze and provide sequences of the IGS rRNA region from different Leishmania spp. and to evaluate their potential as biomarkers to characterize L. braziliensis. A set of primers was designed for complete amplification of the IGS rRNA region of Leishmania spp. PCR products were submitted to Sanger sequencing. The sequences obtained were aligned and analyzed for size and similarity, as well as deposited in GenBank. Characteristics of the repetitive elements (IGSRE) present in the IGS rRNA were also verified. In addition, a set of primers for L. braziliensis identification for qPCR was developed and optimized. Sensitivity (S), specificity (σ), and efficiency (ε) tests were applied. It was found that the mean size for the IGS rRNA region is 3 kb, and the similarity analysis of the sequences obtained demonstrated high conservation among the species. It was observed that the size for the IGSRE repetitive region varies between 61 and 71 bp, and there is a high identity between some species. Fifteen sequences generated for the IGS rRNA partial region of nine different species were deposited in GenBank so far. The specific primer system for L. braziliensis showed S = 10 fg, ε = 98.08%, and logσ = 103 for Leishmania naiffi; logσ = 104 for Leishmania guyanensis; and logσ = 105 for Leishmania shawi. This protocol system can be used for diagnosis, identification, and quantification of a patient's parasite load, aiding in the direction of a more appropriate therapeutic management to the cases of infection by this etiological agent. Besides that, the unpublished sequences deposited in databases can be used for multiple analyses in different contexts.
Copyright © 2020 Tayná C. de Goes et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Figures


References
-
- Lainson R., Shaw J. J. New World leishmaniasis. Topley & Wilson's Microbiology and Microbial Infections. 2010;1 doi: 10.1002/9780470688618.taw0182. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

