Bilateral Traumatic Facial Paralysis with Hearing Impairment and Abducens Palsy
- PMID: 33083077
- PMCID: PMC7563085
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/8843187
Bilateral Traumatic Facial Paralysis with Hearing Impairment and Abducens Palsy
Abstract
The temporal bone is often affected in basilar skull fractures. Fractures involving the petrous portion are particularly significant, as they may be associated with neurovascular sequelae. Bilateral facial paralysis secondary to bilateral temporal bone fracture is a rare clinical entity, even more so when associated with other cranial nerve damage such as abducens nerve paralysis and hearing impairment. Only 4 similar cases have been reported in the literature to date. In this paper, we describe a 28-year-old male patient with bilateral facial paralysis, unilateral abducens palsy, and bilateral hearing loss due to bitemporal fractures that developed after a motor vehicle accident. Conservative management was preferred. The 6-month follow-up showed remarkable improvement. This report highlights the effectiveness of conservative management in posttraumatic complete facial and abducens palsy.
Copyright © 2020 Imane Ouhbi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
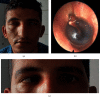
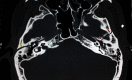

Similar articles
-
Bilateral traumatic facial paralysis associated with unilateral abducens palsy: a case report.J Laryngol Otol. 2005 Feb;119(2):144-7. doi: 10.1258/0022215053419907. J Laryngol Otol. 2005. PMID: 15829070
-
Spontaneous recovery of post-traumatic acute bilateral facial and abducens nerve palsy.Asian J Neurosurg. 2016 Oct-Dec;11(4):446. doi: 10.4103/1793-5482.145056. Asian J Neurosurg. 2016. PMID: 27695556 Free PMC article.
-
[A case of crushing head injury showing bilateral abducens, facial and acoustic nerve palsies].No Shinkei Geka. 1988 Jun;16(7):869-73. No Shinkei Geka. 1988. PMID: 3065670 Review. Japanese.
-
Abducens Nerve Avulsion and Facial Nerve Palsy After Temporal Bone Fracture: A Rare Concomitance of Injuries.World Neurosurg. 2016 Apr;88:689.e5-689.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2015.11.076. Epub 2015 Dec 23. World Neurosurg. 2016. PMID: 26723286
-
Post-traumatic bilateral facial palsy: a case report and literature review.Brain Inj. 2004 Mar;18(3):315-20. doi: 10.1080/0269905031000149489. Brain Inj. 2004. PMID: 14726289 Review.
Cited by
-
The auditory outcomes in non-blast related traumatic brain injury and the role of severity, aetiology and gender: a scoping review.Front Neurol. 2025 Jul 10;16:1589117. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1589117. eCollection 2025. Front Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40708956 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Concomitant abducens and facial nerve palsies following bone temporal fracture: Case report.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2022 Aug 4;80:104318. doi: 10.1016/j.amsu.2022.104318. eCollection 2022 Aug. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2022. PMID: 36045794 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chan E. H., Tan H. M., Tan T. Y. Facial palsy from temporal bone lesions. Annals of the Academy of Medicine, Singapore. 2005;34(4):322–329. - PubMed
-
- Davis R. E., Telischi F. F. Traumatic facial nerve injuries: review of diagnosis and treatment. The Journal of Cranio-Maxillofacial Trauma. 1995;1(3):30–41. - PubMed
-
- Brodie H. A., Thompson T. C. Management of complications from 820 temporal bone fractures. The American Journal of Otology. 1997;18(2):188–197. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

