Bilateral Traumatic Facial Paralysis with Hearing Impairment and Abducens Palsy
- PMID: 33083077
- PMCID: PMC7563085
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/8843187
Bilateral Traumatic Facial Paralysis with Hearing Impairment and Abducens Palsy
Abstract
The temporal bone is often affected in basilar skull fractures. Fractures involving the petrous portion are particularly significant, as they may be associated with neurovascular sequelae. Bilateral facial paralysis secondary to bilateral temporal bone fracture is a rare clinical entity, even more so when associated with other cranial nerve damage such as abducens nerve paralysis and hearing impairment. Only 4 similar cases have been reported in the literature to date. In this paper, we describe a 28-year-old male patient with bilateral facial paralysis, unilateral abducens palsy, and bilateral hearing loss due to bitemporal fractures that developed after a motor vehicle accident. Conservative management was preferred. The 6-month follow-up showed remarkable improvement. This report highlights the effectiveness of conservative management in posttraumatic complete facial and abducens palsy.
Copyright © 2020 Imane Ouhbi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
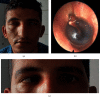
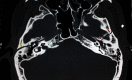

References
-
- Chan E. H., Tan H. M., Tan T. Y. Facial palsy from temporal bone lesions. Annals of the Academy of Medicine, Singapore. 2005;34(4):322–329. - PubMed
-
- Davis R. E., Telischi F. F. Traumatic facial nerve injuries: review of diagnosis and treatment. The Journal of Cranio-Maxillofacial Trauma. 1995;1(3):30–41. - PubMed
-
- Brodie H. A., Thompson T. C. Management of complications from 820 temporal bone fractures. The American Journal of Otology. 1997;18(2):188–197. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

