Hot Aortic Nodules
- PMID: 33083181
- PMCID: PMC7567324
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.10479
Hot Aortic Nodules
Abstract
Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death worldwide. Morbidity of the dreaded thrombotic complications of atherosclerosis such as cerebrovascular accident and myocardial infarction may be severe. Early detection of fulminant disease is therefore important for risk stratification and selecting a treatment strategy. In this report we present four patients in which 18-fluorodeoxyglucose uptake was identified in atherosclerotic plaques at positron emission tomography, performed for other indications. The study aims to showcase the potential implications of 18-fluorodeoxyglucose avid plaques, which may be otherwise overlooked at positron emission tomography. Early detection may aid in prevention of complications of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease through aggressive lifestyle modification, as well as pharmacologic or other intervention, such as endovascular atherectomy.
Keywords: atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease; cerebrovascular accident (stroke); fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography; inflammatory plaques; myocardial infarction; plaque rupture.
Copyright © 2020, Soule et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
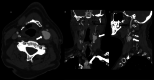
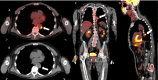
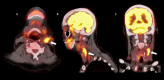

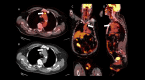
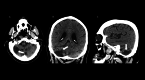

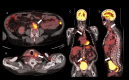
References
-
- Global overview of the epidemiology of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Barquera S, Pedroza-Tobias A, Medina C, Hernandez-Barrera L, Bibbins-Domingo K, Lozano R, Moran A. Arch Med Res. 2015;46:328–338. - PubMed
-
- Pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Falk E. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006;47:7–12. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
