Efficacy of Pumpkin Ointment in Treatment of Chronic Hand Eczema: A Randomized, Active-Controlled, Double Blind Clinical Trial
- PMID: 33083301
- PMCID: PMC7548497
- DOI: 10.18502/ijph.v49i7.3588
Efficacy of Pumpkin Ointment in Treatment of Chronic Hand Eczema: A Randomized, Active-Controlled, Double Blind Clinical Trial
Abstract
Background: Hand Eczema (HE) is chronic skin disease with a high prevalence in population. It has negative impact on the quality of life. Due to the public interest in herbal remedies, we attempt to assess the efficacy of pumpkin ointment in treatment of chronic HE in this research.
Methods: This study was conducted in an outpatient clinic at Imam-Khomeini Hospital in Tehran (Iran) from May 2015 to Nov 2016. We performed a double-blind trial on 60 patients with chronic HE randomized to four groups included pumpkin, betamethasone, eucerin and almond ointment (n=15 for each group) for 28 days. Patients were ordered to apply ointments twice a day. Hand Eczema Severity Index (HECSI) and Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI) of the patients were evaluated by a dermatologist on the 1st, 14th and 28th d after the start of treatment.
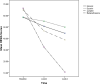
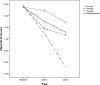
Results: Patients' DLQI scores in pumpkin and betamethasone group was significant and pumpkin group showed a better response in quality of life (P=0.001). Betamethasone and pumpkin ointment were effective and showed significant improvement compared with almond and eucerin and reduce HECSI scores (P=0.002 and P=0.012 respectively). Betamethasone ointment outcome on HECSI scores in comparison with topical pumpkin was significant (P<0.001). No clinically adverse effects were observed.
Conclusion: Although pumpkin ointment showed a better response in patients' DLQI in HE but it was less effective than betamethasone in decreasing HECSI.
Keywords: Almond; Betamethasone; Hand eczema; Persian; Pumpkin; Traditional medicine.
Copyright© Iranian Public Health Association & Tehran University of Medical Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Diepgen TL, Agner T, Aberer W, et al. (2007). Management of chronic hand eczema. Contact Dermatitis, 57:203–10. - PubMed
-
- de Leon FJ, Berbegal L, Silvestre JF. (2015). Management of Chronic Hand Eczema. Actas Dermosifiliogr, 106:533–44. - PubMed
-
- Diepgen TL. (2003). Occupational skin-disease data in Europe. Int Arch Occup Environ Health, 76:331–8. - PubMed
-
- Skoet R, Zachariae R, Agner T. (2003). Contact dermatitis and quality of life: a structured review of the literature. Br J Dermatol, 149:452–6. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources