Role of monoclonal antibody drugs in the treatment of COVID-19
- PMID: 33083387
- PMCID: PMC7559676
- DOI: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i19.4280
Role of monoclonal antibody drugs in the treatment of COVID-19
Abstract
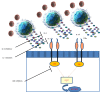
Currently clinicians all around the world are experiencing a pandemic caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The clinical presentation of this pathology includes fever, dry cough, fatigue and acute respiratory distress syndrome that can lead to death infected patients. Current studies on coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) continue to highlight the urgent need for an effective therapy. Numerous therapeutic strategies have been used until now but, to date, there is no specific effective treatment for SARS-CoV-2 infection. Elevated inflammatory cytokines have been reported in patients with COVID-19. Evidence suggests that elevated cytokine levels, reflecting a hyperinflammatory response secondary to SARS-CoV-2 infection, are responsible for multi-organ damage in patients with COVID-19. For these reason, numerous randomized clinical trials are currently underway to explore the effectiveness of biopharmaceutical drugs, such as, interleukin-1 blockers, interleukin-6 inhibitors, Janus kinase inhibitors, in COVID-19. The aim of the present paper is to briefly summarize the pathogenetic rationale and the state of the art of therapeutic strategy blocking hyperinflammation.
Keywords: Anakinra; Baricitinib; Canakinumab; Clazakizumab; Ruxolitinib; Sarilumab; Siltuximab; Tocilizumab; Tofacitinib.
©The Author(s) 2020. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: Authors declare no conflict of interests for this article.
Figures
References
-
- Barone M, Ucciferri C, Cipollone G, Mucilli F. Recombinant Human Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 and COVID-19 Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: A Theoretical or a Real Resource? EJMO. 2020;4:139–140.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous